

基于新闻大数据的北极地区地缘关系研究
|
李萌(1995-), 女, 山西阳泉人, 硕士生, 主要从事基于时空语义普遍关联的大数据分析。E-mail: limeng18@mails.ucas.ac.cn |
收稿日期: 2019-07-20
要求修回日期: 2020-04-28
网络出版日期: 2021-07-25
基金资助
中国科学院战略性先导科技专项(XDA23100103)
中国科学院重点部署项目(ZDRW-ZS-2017-4)
版权
Big data analysis on geographical relationship of the Arctic based on news reports
Received date: 2019-07-20
Request revised date: 2020-04-28
Online published: 2021-07-25
Supported by
The Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences(XDA23100103)
The Key Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences(ZDRW-ZS-2017-4)
Copyright
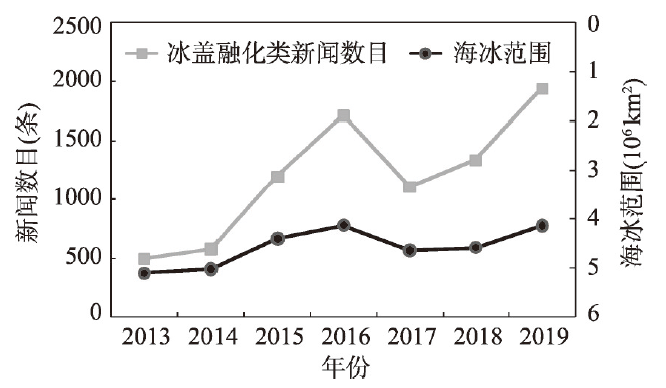
随着全球气候变暖,北极地区海冰大面积消融,引发了严重环境问题,同时使得北极航道成为可能,北极地区的战略地位显著提升。作为近北极国家,北极地区国际关系变化对中国的北极政策有直接影响。全面实时地分析北极地区地缘关系及其变化特征,对中国制定北极地区的政治、经济、外交政策具有重要指导作用。海量全球实时开放数据库的出现以及大数据技术的发展,如GDELT新闻事件数据库提供了覆盖全世界的源于各国主要媒体服务平台的新闻数据,为地缘关系实时监控及分析提供了可能性。本文利用GDELT数据库,引入labeled- LDA主题分析的理论与方法,挖掘了2013—2019年北极圈内8个国家和地区社会发展关键要素,构建了国家(地区)交互网络,发现了北极地区国家(地区)之间关系的演变格局。主要结论为:① 北极地区热点新闻主题聚焦于气候变化/冰盖融化,冰盖融化是北极地缘关系变化的主要驱动因子;② 冰盖融化新闻热度与海冰监测数据变化存在极强的相关性;③ 随着冰盖融化,北极地区的社会经济军事活动激增,其主导权的争夺日趋激烈,总体呈现出俄罗斯、加拿大主导的格局。
李萌 , 袁文 , 袁武 , 牛方曲 , 李汉青 , 胡段牧 . 基于新闻大数据的北极地区地缘关系研究[J]. 地理学报, 2021 , 76(5) : 1090 -1104 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202105004
Global warming has caused a shrinkage of the Arctic sea ice cover. It endangered the environment, but made the Arctic channel possible. Therefore, the strategic position of the Arctic has been improved significantly. As a near-Arctic country, China has formulated relevant Arctic policies, which will be directly affected by the changes in the international relations between the eight Arctic countries (region). A comprehensive and real-time analysis on the variation characteristics of the Arctic geographical relationship is required in China, which can provide instructions for formulating political, economic and diplomatic countermeasures in the Arctic. Massive global real-time open databases, such as GDELT (The Global Database of Events, Language, and Tone) global news event database, provide news data from major media in various countries. And this makes it possible to monitor the geographical relationship in real time. Based on the GDELT database and the method of labeled-LDA (Latent Dirichlet Allocation), this paper explored the key elements in social development of eight Arctic countries (region) over the past seven years. This paper also constructed the national interaction network, and identified the evolution pattern of the relations between the Arctic countries. The following conclusions were drawn: (1) Arctic news focused on climate change and ice sheet melting, which had become the main driving factor for the change of international relations in the Arctic; (2) There was a strong correlation between the number of ice sheet melting news pieces and the sea ice area; (3) With the melting of the ice sheet, the social, economic and military activities in the Arctic were booming, and the competition for dominance was becoming increasingly fierce. Generally, a pattern dominated by Russia and Canada was formed.

表1 GDELT事件类型Tab. 1 GDELT event type |
| 事件类型 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 发表公开声明 | 上诉 | 表示合作意向 | 咨询 | 进行外交合作 |
| 需求 | 提供援助 | 产出 | 调查 | 进行物质合作 |
| 不被通过 | 拒绝 | 威胁 | 抗议 | 展示武力姿态 |
| 减少关系 | 胁迫 | 攻击 | 战斗 | 使用非常规的处理方式 |
表2 2013—2019年北极地区新闻频次分主题统计(条)Tab. 2 Statistics on the number of news pieces in the Arctic by topic, 2013-2019 |
| 年份 | 动物保护 | 航运交通 | 气候变化 | 经济活动 | 军事活动 | 区域治理 | 资源开发 | 冰盖融化 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2013 | 324 | 398 | 766 | 625 | 1803 | 712 | 773 | 499 |
| 2014 | 671 | 575 | 977 | 1336 | 5422 | 1120 | 953 | 580 |
| 2015 | 956 | 2381 | 1625 | 1045 | 3616 | 1342 | 1434 | 1199 |
| 2016 | 1447 | 3915 | 1377 | 1195 | 3923 | 1476 | 1028 | 1716 |
| 2017 | 1029 | 1603 | 1326 | 832 | 4080 | 1460 | 943 | 1109 |
| 2018 | 1280 | 1193 | 2147 | 933 | 3244 | 1270 | 930 | 1338 |
| 2019 | 1589 | 1537 | 3591 | 991 | 4605 | 3162 | 1220 | 1940 |
表3 2013—2019年北极地区各新闻主题对应的高频词Tab. 3 High frequency words corresponding to each news topic in the Arctic from 2013 to 2019 |
| 事件 | top1 | top 2 | top 3 | top 4 | top 5 | top 6 | top 7 | top 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 冰盖融化 | ice | climate | glacier | sheet | cap | record | researcher | melting |
| 动物保护 | bear | polar | wildlife | climate | animal | ice | conservation | study |
| 航运交通 | ship | cruise | ice | polar | route | coast | expedition | Norwegian |
| 区域治理 | policy | development | region | oil | country | paper | cooperation | state |
| 气候变化 | climate | temperature | cold | weather | record | degree | polar | wind |
| 资源开发 | energy | oil | fuel | drilling | fossil | gas | company | climate |
| 经济活动 | oil | market | price | natural | industry | company | car | gas |
| 军事活动 | military | defense | force | state | missile | Nordic | war | logistics |
表4 2013—2019年北极地区各新闻主题相关系数Tab. 4 The correlation coefficient of various news topics in the Arctic from 2013 to 2019 |
| 动物保护 | 航运交通 | 气候变化 | 经济活动 | 军事活动 | 区域治理 | 资源开发 | 冰盖融化 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 动物保护 | 1 | 0.621688 | 0.774918 | 0.323984 | 0.398627 | 0.758592 | 0.443681 | 0.970136 |
| 航运交通 | 0.621688 | 1 | 0.11132 | 0.37161 | 0.128924 | 0.205274 | 0.459066 | 0.668356 |
| 气候变化 | 0.774918 | 0.11132 | 1 | 0.042325 | 0.284297 | 0.924086 | 0.491428 | 0.797022 |
| 经济活动 | 0.323984 | 0.37161 | 0.042325 | 1 | 0.815929 | 0.150709 | 0.353416 | 0.206339 |
| 军事活动 | 0.398627 | 0.128924 | 0.284297 | 0.815929 | 1 | 0.462412 | 0.333612 | 0.261695 |
| 区域治理 | 0.758592 | 0.205274 | 0.924086 | 0.150709 | 0.462412 | 1 | 0.500057 | 0.794655 |
| 资源开发 | 0.443681 | 0.459066 | 0.491428 | 0.353416 | 0.333612 | 0.500057 | 1 | 0.513771 |
| 冰盖融化 | 0.970136 | 0.668356 | 0.797022 | 0.206339 | 0.261695 | 0.794655 | 0.513771 | 1 |
图3 2013—2019年北极地区“军事活动”国家(地区)交互网络时序变化Fig. 3 Changes of national interaction network of military activity in the Arctic from 2013 to 2019 |
图5 2013—2019年北极地区“气候变化”国家(地区)交互网络时序变化Fig. 5 Changes of national interaction network of climate change in the Arctic from 2013 to 2019 |
图6 2013—2019年北极地区“冰盖融化”国家(地区)交互网络时序变化Fig. 6 Changes of national interaction network of shrunken ice sheet theme from 2013 to 2019 |
图8 2013—2019年北极地区“资源开发”国家(地区)交互网络时序变化Fig. 8 Changes of national interaction network of resource development in the Arctic from 2013 to 2019 |
表5 2019年北极地区(地区)国家交互网络情感分析结果(条)Tab. 5 Sentiment analysis of national interaction networks in the Arctic in 2019 (piece) |
| 交互 | 非常消极 | 消极 | 中性 | 积极 | 非常积极 | 交互 | 非常消极 | 消极 | 中性 | 积极 | 非常积极 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 加拿大—俄罗斯 | 1 | 125 | 2351 | 21 | 0 | 芬兰—瑞典 | 0 | 10 | 893 | 10 | 0 |
| 挪威—俄罗斯 | 0 | 54 | 2107 | 20 | 0 | 加拿大—瑞典 | 0 | 18 | 857 | 1 | 0 |
| 丹麦—格陵兰岛 | 0 | 10 | 1848 | 7 | 0 | 格陵兰岛—挪威 | 0 | 4 | 818 | 19 | 1 |
| 加拿大—格陵兰岛 | 1 | 27 | 1568 | 18 | 0 | 冰岛—俄罗斯 | 0 | 5 | 815 | 12 | 0 |
| 格陵兰岛—俄罗斯 | 0 | 41 | 1485 | 11 | 0 | 丹麦—瑞典 | 0 | 10 | 754 | 12 | 0 |
| 丹麦—俄罗斯 | 0 | 9 | 1435 | 8 | 0 | 格陵兰岛—冰岛 | 1 | 25 | 686 | 20 | 0 |
| 加拿大—挪威 | 0 | 12 | 1394 | 17 | 0 | 加拿大—芬兰 | 0 | 45 | 647 | 8 | 2 |
| 芬兰—俄罗斯 | 0 | 72 | 1301 | 4 | 0 | 加拿大—冰岛 | 1 | 8 | 632 | 16 | 0 |
| 挪威—瑞典 | 0 | 18 | 1136 | 14 | 0 | 丹麦—芬兰 | 0 | 4 | 637 | 8 | 1 |
| 俄罗斯—瑞典 | 0 | 29 | 1046 | 3 | 0 | 丹麦—冰岛 | 0 | 3 | 624 | 12 | 0 |
| 丹麦—挪威 | 0 | 7 | 957 | 19 | 0 | 芬兰—冰岛 | 0 | 3 | 523 | 14 | 0 |
| 加拿大—丹麦 | 0 | 5 | 953 | 10 | 0 | 冰岛—瑞典 | 0 | 7 | 487 | 8 | 0 |
| 冰岛—挪威 | 0 | 7 | 916 | 28 | 0 | 格陵兰岛—瑞典 | 2 | 15 | 412 | 0 | 0 |
| 芬兰—挪威 | 1 | 23 | 903 | 16 | 0 | 芬兰—格陵兰岛 | 0 | 8 | 380 | 1 | 0 |
注:数值为国家(地区)交互网络中不同情感类别新闻数;情感得分属于[-100, -10)为“非常消极”,属于[-10, -5)为“消极”,属于[-5, 5)为“中性”,属于[5, 10)为“积极”,属于[10, 100]为“非常积极”;表格按新闻总数降序排列。 |
| [1] |
[ 叶滨鸿, 程杨, 王利, 等. 北极地区地缘关系研究综述. 地理科学进展, 2019,38(4):489-505.]
|
| [2] |
[ 杜德斌, 秦大河, 马亚华, 等. 冰冻圈地缘政治时代的到来. 中国科学院院刊, 2020,35(4):514-522.]
|
| [3] |
[ 何奇松. 气候变化与北极地缘政治博弈. 外交评论(外交学院学报), 2010,27(5):113-122.]
|
| [4] |
[ 关晓光, 李振福. “冰上丝绸之路”对中国与沿线北极国家的经济效应研究. 大连理工大学学报(社会科学版), 2021,42(1):45-57.]
|
| [5] |
[ 熊琛然, 王礼茂, 梁茂林. “冰上丝绸之路”建设与中国的地缘战略意义. 学术探索, 2018,12:26-32.]
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
[ 李振福. 大北极国家网络及中国的大北极战略研究. 东北亚论坛, 2015,24(2):31-44, 127.]
|
| [9] |
[ 谢晓光, 程新波. 俄罗斯北极政策调整背景下的“冰上丝绸之路”建设. 辽宁大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 2019,47(1):184-192.]
|
| [10] |
[ 郭培清, 王俊杰. 格陵兰独立问题的地缘政治影响. 现代国际关系, 2017(8):58-64.]
|
| [11] |
[ 肖洋. 格陵兰:丹麦北极战略转型中的锚点? 太平洋学报, 2018,26(6):78-86.]
|
| [12] |
[ 朱宝林. 解读加拿大的北极战略: 基于中等国家视角. 世界经济与政治论坛, 2016(4):141-155.]
|
| [13] |
[ 叶滨鸿, 程杨, 王利, 等. 北极地区地缘经济关系演变研究. 世界地理研究, 2021,30(2):234-244.]
|
| [14] |
[ 黄季夏, 张天媛, 王利, 等. 俄罗斯油气资源空间分布格局及可达性评估. 地理学报, 2020,75(9):2009-2024.]
|
| [15] |
[ 程昌秀, 史培军, 宋长青, 等. 地理大数据为地理复杂性研究提供新机遇. 地理学报, 2018,73(8):1397-1406.]
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
[ 马明清, 袁武, 葛全胜, 等. “一带一路”若干区域社会发展态势大数据分析. 地理科学进展, 2019,38(7):1009-1020.]
|
| [18] |
[ 陈小强, 袁丽华, 沈石, 等. 中国及其周边国家间地缘关系解析. 地理学报, 2019,74(8):1534-1547.]
|
| [19] |
[ 徐广淼. 变动世界中的北极秩序: 生成机制与变迁逻辑. 俄罗斯东欧中亚研究, 2021,1: 106-124, 157-158.]
|
| [20] |
[ 王鹏, 高铖, 陈晓美. 基于LDA模型的文本聚类研究. 情报科学, 2015,33(1):63-68.]
|
| [21] |
[ 李文波, 孙乐, 张大鲲. 基于Labeled-LDA模型的文本分类新算法. 计算机学报, 2008,31(4):620-627.]
|
| [22] |
[ 孙迁杰, 马建光. 论北极地缘政治博弈中俄罗斯的威慑战略. 上海交通大学学报(哲学社会科学版), 2017,25(1):14-21.]
|
| [23] |
[ 刘大海, 马云瑞, 王春娟, 等. 全球气候变化环境下北极航道资源发展趋势研究. 中国人口·资源与环境, 2015,25(Suppl.1):6-9.]
|
| [24] |
[ 罗英杰, 李飞. 大国北极博弈与中国北极能源安全: 兼论“冰上丝绸之路”推进路径. 国际安全研究, 2020,38(2):91-115, 159.]
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
[ 沈心仪, 张瑜, 陈长胜, 等. 加拿大北极群岛区域西北航道海冰冰情长期时空变化特征研究. 极地研究, 2021,33(1):71-87.]
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |