

过去1500 a亚洲夏季风降水的强迫特征
|
王志远(1984-), 男, 内蒙古通辽人, 博士, 讲师, 主要从事全球环境变化与古气候模拟研究。E-mail: wzhy@zjnu.edu.cn |
收稿日期: 2020-01-04
要求修回日期: 2020-10-14
网络出版日期: 2021-05-25
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(41901095)
版权
The forced response of Asian summer monsoon precipitation during the past 1500 years based on the CESM
Received date: 2020-01-04
Request revised date: 2020-10-14
Online published: 2021-05-25
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(41901095)
Copyright
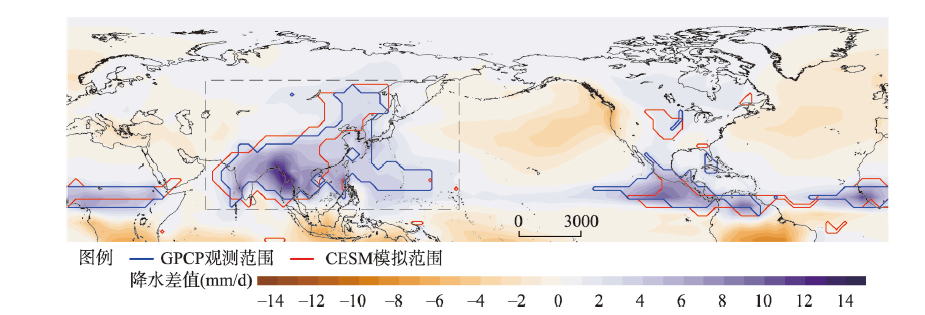
基于通用地球系统模式(CESM)进行了4组长达1500 a的模拟试验(全强迫试验,控制试验,自然外强迫试验和人类活动外强迫试验)。在评估模式模拟亚洲夏季风降水可靠性的基础上,对模拟结果进行10~100 a的带通滤波以获取年代—百年际亚洲夏季风降水信号。主要结论为:① 过去1500 a亚洲夏季风降水强度存在显著的约15 a、25 a、40 a和70 a的年代—百年际周期信号;② 年代—百年际亚洲夏季风降水的主要时空变化模态表现为外强迫模态和气候系统内部变化模态;③ 过去1500 a亚洲夏季风降水的强迫模态表现为经向“三明治”结构,即中国北方季风区和热带季风区同向变化,而在东亚中纬度一带季风降水反向变化特征。这种降水的空间分布模态主要由自然外强迫(太阳辐射+火山活动)作用所导致。本文为历史时期亚洲季风降水变化的研究提供了材料支撑,为全球变暖背景下亚洲季风降水演变提供参考。
王志远 , 王江林 , 贾佳 , 刘健 . 过去1500 a亚洲夏季风降水的强迫特征[J]. 地理学报, 2021 , 76(3) : 550 -565 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202103005
Asian summer monsoon (ASM), one of the key elements of the global climate system, strongly affects food production and security of most people over Asia. However, the characteristics and the forcing drivers of the ASM system at decadal to centennial time scales remain unclear. To address these issues, we report four 1500-a long climate model simulations based on the Community Earth System Model (CESM), including full-forced run (ALLR), control run (CTRL), natural run (NAT), and anthropogenic run (ANTH). After evaluating the performances of the CESM in simulating ASM precipitation, a 10-100 bandpass filter is applied to obtain the decadal-centennial signals in ASM precipitation. The main conclusions are as follows: (1) the variation of ASM intensity shows significant decadal to centennial periodicities in the ALLR, such as ~15, ~25, ~40 and ~70 years. (2) The major spatial-temporal distributions of ASM precipitation in the ALLR show an external forced mode and a climate internal variability mode. (3) The leading forced mode of ASM precipitation is mainly affected by natural forcing over the past 1500 years and characterizes a meridional spatial 'triple' mode. In the NAT (solar irradiation and volcanic eruptions), the substantial warming (cooling) over the western tropical Pacific enhances (or reduces) the SST gradient change in the tropical Pacific and modifies the ASM rainfall distribution. Our findings contribute to a better understanding of the ASM in the past and provide implications for future projections of the ASM under global warming.

Key words: ASM; decadal-centennial timescales; CESM; past 1500 years; forced mode
表1 本文4组试验的具体设置Tab. 1 Details of experimental design |
| 序号 | 试验名称 | 强迫条件(年份) | 时间(a) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 全称 | 简称 | TSI | VOL | GHGs | LULC | Orb | |||
| 1 | 控制试验 | CTRL | 1850 | 1850 | 1850 | 1850 | 1990 | 1~2000 | |
| 2 | 全强迫试验 | ALLR | √ | √ | √ | √ | √ | 1~2000 | |
| 3 | 自然外强迫试验 | NAT | √ | √ | 1850 | 1850 | 1990 | 1~2000 | |
| 4 | 人类活动外强迫试验 | ANTH | 1850 | 1850 | √ | √ | 1990 | 1~2000 | |
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
[ 周鑫, 郭正堂, 秦利. 近百年来自然和人为因素对亚洲季风降水影响的时间序列分析研究. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2010,40(12):1718-1724.]
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
|
| [83] |
|
| [84] |
|
| [85] |
|
| [86] |
|
| [87] |
|
| [88] |
|
| [89] |
|
| [90] |
|
| [91] |
|
| [92] |
|
| [93] |
|
| [94] |
|
| [95] |
|
| [96] |
|
| [97] |
|
| [98] |
|
| [99] |
|
| [100] |
|
| [101] |
|
| [102] |
|
| [103] |
|
| [104] |
|
| [105] |
|
| [106] |
|
| [107] |
|
| [108] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |