

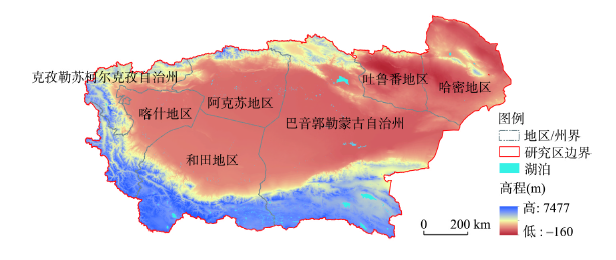
新疆南部地区风沙扩散风险评价及景观格局优化
|
史娜娜(1983-), 女, 山东潍坊人, 硕士, 工程师, 主要从事生态系统与生物多样性评估。E-mail: shinn123@163.com |
收稿日期: 2019-12-15
要求修回日期: 2020-10-27
网络出版日期: 2021-03-25
基金资助
生态环境部生物多样性保护专项(2020)()
版权
Risk assessment of sandstorm diffusion and landscape pattern optimization in southern Xinjiang
Received date: 2019-12-15
Request revised date: 2020-10-27
Online published: 2021-03-25
Supported by
The Biodiversity Survey and Assessment Project of the Ministry of Ecology and Environment (2020)()
Copyright
基于“致灾因子—孕灾环境—承灾体”3个维度,利用空间主成分分析法(SPCA)开展新疆南部地区风沙扩散风险评价,然后借助最小累积阻力模型(MCR)优化关键景观格局组分,构建多层次生态网络。结果表明:① 区域致灾因子危险性较高,孕灾环境较为脆弱;和静县、阿合奇县生态本底较好,而盆地及其南部各县易于风沙扩散,尤其是和田地区、且末县及若羌县;绿洲人口和农业生产高度聚集,易损性较大。② 46.53%的区域沙源丰富,立地条件差,风沙扩散风险较高。区域下垫面植被覆盖度和土壤类型是影响风沙扩散的最主要因素,风场强度是区域沙源扩散的主要诱因。③ 基于MCR模型,构建20条生态廊道连通生态源地,包括5条河流型、9条道路型和6条绿带型廊道;其中,1号和4号廊道纵贯塔克拉玛干沙漠,其余廊道沿塔里木盆地外缘呈圆环形分布;同时,判别出30个生态节点,包括A类生态节点7个,B类生态节点23个,主要分布在和田地区和巴州,可以通过建设防护林带、提高地表植被覆盖等措施降低风沙扩散风险。研究结果为中国北方干旱、半干旱地区风沙扩散风险防控与景观格局优化提供了技术支撑。
关键词: 风沙扩散风险评价; 景观格局; 空间主成分分析(SPCA); 最小累积阻力模型(MCR); 新疆南部地区
史娜娜 , 韩煜 , 王琦 , 汉瑞英 , 高晓奇 , 赵志平 , 刘高慧 , 肖能文 . 新疆南部地区风沙扩散风险评价及景观格局优化[J]. 地理学报, 2021 , 76(1) : 73 -86 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202101006
Based on the three dimensions of "hazard-formative factors, hazard-formative environments, hazard-affected bodies", we assessed the risk of sandstorm diffusion in the southern Xinjiang using the Spatial Principal Component Analysis (SPCA) method. A multi-level ecological network was built and components of key landscape patterns were optimized by the Minimum Cumulative Resistance (MCR) model. (1) The risk of hazard was high in this region by single dimension factor analysis. Under the action of wind, eight sandstorm source areas and Tarim Basin were prone to sandstorm diffusion because of the existence of abundant sand materials. The hazard-formative environment was relatively fragile. Hejing and Aheqi counties had relatively good ecological background. In the Tarim Basin and its southern counties, the sandstorm tends to spread, especially in Hotan Prefecture, and counties of Qiemo and Ruoqiang. Oasis population and agricultural production were highly concentrated and vulnerable to environmental factors. (2) Some 46.53% of the area had high risk of sand diffusion due to abundant sand sources and poor site conditions. The most important factors affecting the wind sand diffusion were vegetation coverage and soil types of the underlying surface. The main causes of regional sand source diffusion were the intensity of wind field. (3) Based on the MCR model, 20 ecological corridors were constructed to connect ecological source areas, including five river types, nine road types and six green belt types of corridors. Among them, corridors 1 and 4 connected via Taklimakan Desert, and the rest of the corridors presented a circular distribution pattern at the outer edge of Tarim Basin. At the same time, 30 ecological nodes were identified, including seven class-A ecological nodes and 23 class-B ecological nodes, which were mainly distributed in Hotan and Bayingolin prefectures. The risk of sandstorm diffusion can be reduced by constructing shelterbelts and improving vegetation coverage. Results provide technical support for the prevention and control of sandstorm diffusion and the optimization of landscape patterns in the arid and semi-arid areas of northern China.

表1 风沙扩散影响因子分级依据Tab. 1 The evaluation standard of sandstorm diffusion factors |
| 分级 | 风场强度(kg/m) | 干燥度 | 湿润指数 | 植被覆盖度(%) | 土壤侵蚀 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | < 50 | < 20 | 450 | > 70 | 微度 |
| 2 | 50~100 | 20~40 | 30~40 | 50~70 | 轻度 |
| 3 | 100~500 | 40~60 | 20~30 | 20~50 | 中度 |
| 4 | 500~1000 | 60~80 | 10~20 | 5~20 | 强度 |
| 5 | > 1000 | > 80 | < 10 | < 5 | 极强度 |
| 分级 | 土壤类型 | 土地利用 | 人口(万人) | GDP(亿元) | 农田面积 |
| 1 | 湖泊水库等 | 林地、建设用地 | < 8 | < 20 | 有 |
| 2 | 草甸土、灌淤土 | 中高覆盖度草地 | 8~15 | 20~30 | 无 |
| 3 | 石质土、棕漠土 | 低覆盖草地、耕地、滩地 | 15~25 | 30~60 | |
| 4 | 新积土、粗骨土 | 沼泽地、盐碱地 | 25~35 | 60~100 | |
| 5 | 风沙土 | 沙地、裸土地 | > 35 | > 100 |
表2 主成分载荷矩阵Tab. 2 Load matrix of principal components |
| 维度 | 指标 | 主成分 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | ||
| 致灾因子 | 风场强度 | -0.235 | 0.018 | -0.155 | -0.267 | -0.090 | 0.603 | -0.034 | 0.350 | 0.588 | -0.089 |
| 干燥度 | -0.652 | -0.199 | 0.468 | 0.090 | 0.488 | 0.165 | -0.023 | 0.027 | -0.200 | 0.021 | |
| 湿润指数 | -0.059 | 0.069 | 0.102 | -0.026 | 0.082 | -0.313 | -0.667 | -0.084 | 0.411 | 0.505 | |
| 孕灾环境 | 植被覆盖度 | 0.027 | 0.561 | -0.266 | 0.618 | 0.264 | 0.193 | -0.141 | 0.293 | -0.128 | 0.056 |
| 土壤侵蚀 | 0.258 | -0.182 | 0.296 | 0.542 | 0.120 | 0.084 | 0.180 | -0.345 | 0.549 | -0.210 | |
| 土壤类型 | 0.493 | -0.036 | 0.223 | -0.197 | 0.160 | 0.535 | -0.473 | -0.187 | -0.290 | -0.107 | |
| 土地利用 | 0.104 | -0.069 | 0.017 | 0.054 | -0.078 | 0.358 | 0.395 | -0.139 | -0.076 | 0.816 | |
| 承灾体 | 人口 | -0.043 | 0.768 | 0.467 | -0.284 | -0.067 | -0.025 | 0.219 | -0.210 | 0.099 | -0.049 |
| GDP | 0.438 | -0.068 | 0.224 | -0.208 | 0.480 | -0.226 | 0.231 | 0.594 | 0.120 | 0.093 | |
| 耕地面积 | -0.031 | 0.081 | -0.518 | -0.280 | 0.630 | -0.020 | 0.141 | -0.462 | 0.118 | -0.026 | |
| [1] |
[ 王森, 王雪姣, 陈东东, 等. 1961—2017年南疆地区沙尘天气的时空变化特征及影响因素分析. 干旱区资源与环境, 2019,33(9):81-86.]
|
| [2] |
[ 管梦鸾, 张正偲, 董治宝. 基于RS和GIS的河西走廊风沙灾害风险评估. 中国沙漠, 2017,37(5):830-835.]
|
| [3] |
[ 王计平. 北京地区风沙扩散风险评价与景观格局优化研究[D]. 北京林业大学, 2007.]
|
| [4] |
[ 李诚志. 新疆沙漠化监测与预警研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆大学, 2012.]
|
| [5] |
[ 李青圃, 张正栋, 万露文, 等. 基于景观生态风险评价的宁江流域景观格局优化. 地理学报, 2019,74(7):1420-1437.]
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
[ 陈小平, 陈文波. 鄱阳湖生态经济区生态网络构建与评价. 应用生态学报, 2016,27(5):1611-1618.]
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
[ 付梦娣, 罗建武, 田瑜, 等. 基于最小累积阻力模型的自然保护区网络构建与优化: 以秦岭地区为例. 生态学杂志, 2018,37(4):1135-1143.]
|
| [12] |
[ 陈昕, 彭建, 刘焱序, 等. 基于“重要性—敏感性—连通性”框架的云浮市生态安全格局构建. 地理研究, 2017,36(3):471-484.]
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
[ 李连香, 许迪, 程先军, 等. 基于分层构权主成分分析的皖北地下水水质评价研究. 资源科学, 2015,37(1):61-67.]
|
| [15] |
[ 万的军, 穆桂金, 雷加强, 等. 塔里木盆地南缘近54年沙尘天气的变化特征及其未来趋势预测. 干旱区资源与环境, 2009,23(9):78-84.]
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
[ 刘纪远, 宁佳, 匡文慧, 等. 2010—2015年中国土地利用变化的时空格局与新特征. 地理学报, 2018,73(5):789-802.]
|
| [18] |
[ 王琦, 付梦娣, 魏来, 等. 基于源—汇理论和最小累积阻力模型的城市生态安全格局构建: 以安徽省宁国市为例. 环境科学学报, 2016,36(12):4546-4554.]
|
| [19] |
[ 史娜娜, 韩煜, 王琦, 等. 青海省保护地生态网络构建与优化. 生态学杂志, 2018,37(6):1910-1916.]
|
| [20] |
[ 蒙吉军, 王雅, 王晓东, 等. 基于最小累积阻力模型的贵阳市景观生态安全格局构建. 长江流域资源与环境, 2016,25(7):1052-1061.]
|
| [21] |
[ 陈利顶, 傅伯杰, 赵文武. “源”“汇”景观理论及其生态学意义. 生态学报, 2006,26(5):1444-1449.]
|
| [22] |
[ 傅博杰, 陈利顶, 马克明, 等. 景观生态学原理及应用. 2版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2011.]
|
| [23] |
[ 岳健, 阿力木江·牙生, 蓝利, 等. 新疆沙漠化防治区划指标和方法. 干旱区研究, 2010,27(2):309-318.]
|
| [24] |
[ 阿力木江·牙. 新疆沙质荒漠化防治区划及分区防治模式. 北京: 中国林业出版社, 2013.]
|
| [25] |
[ 彭建, 李慧蕾, 刘焱序, 等. 雄安新区生态安全格局识别与优化策略. 地理学报, 2018,73(4):701-710.]
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |