

西北内陆河流域“自然—社会—贸易”三元水循环模式解析
|
邓铭江(1960-), 男, 湖南耒阳人, 博士, 教授级高级工程师, 中国工程院院士, 主要从事干旱区水资源研究与水利工程建设管理工作。E-mail: xjdmj@163.com |
收稿日期: 2019-04-08
要求修回日期: 2020-05-14
网络出版日期: 2020-09-25
基金资助
国家重点研发计划(2017YFC0404301)
国家自然科学基金项目(51479209)
版权
Theoretical analysis of "natural-social-trading" ternary water cycle mode in the inland river basin of Northwest China
Received date: 2019-04-08
Request revised date: 2020-05-14
Online published: 2020-09-25
Supported by
National Key R&D Program(2017YFC0404301)
National Natural Science Foundation of China(51479209)
Copyright
持续的强人类活动大大改变了流域水循环演变的结构、路径和驱动力,后者又反过来影响着人类生存发展的水安全。日益深入的市场经济使人类活动对水循环的影响从一个流域扩展到流域之外更宽广的区域范围,以产品贸易为纽带的水“流动”已成为驱动区域水循环演变与影响区域水安全的重要内在因素。以流域为单元的传统水循环研究,难以揭示不同区域之间的水循环联系、双向回馈机制与协同进化机理。本文从西北内陆河流域长期大量输出高耗水农产品这一现象分析入手,采用理论解析与案例相结合方法,阐述分析内陆河流域自然水循环、“自然—社会”二元水循环、区域间贸易水循环的基本过程、显著特征及其驱动机制,继而首次明确提出内陆河流域“自然—社会—贸易”三元水循环模式,并就其通量计量模型、影响因素与生态环境效应、科学前沿进行了探索分析,以便未来西北内陆河水循环、水文水资源等研究能更多重视对驱动内陆河流域水循环的外部力量及其双向互馈、协同进化的分析,更新内陆河流域水安全、生态安全的思考范式。
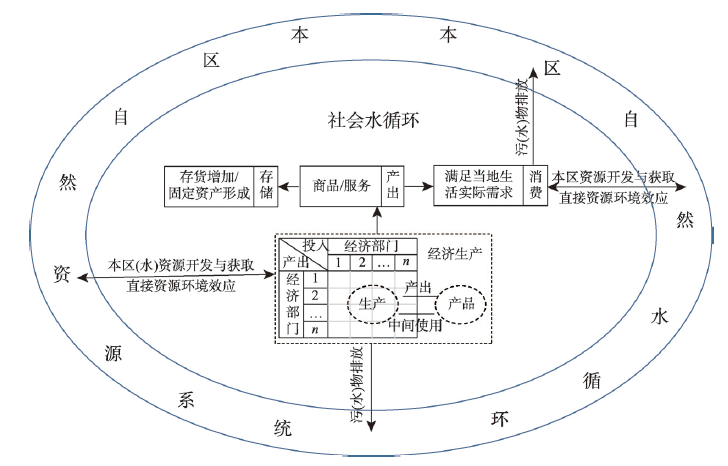
关键词: 西北内陆河流域; 贸易水循环; “自然—社会—贸易”三元水循环模式; 框架解析; 通量平衡模型
邓铭江 , 龙爱华 , 李江 , 邓晓雅 , 张沛 . 西北内陆河流域“自然—社会—贸易”三元水循环模式解析[J]. 地理学报, 2020 , 75(7) : 1333 -1345 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202007001
The continuous and intense human activities have greatly changed the structure, path and driving force of the natural water cycle evolution, which conversely influences the water security of human being. With the process of globalization and market economy, human activities not only affect the artificial development of water and soil resources, but also extend to the economic field. The "flow" of water trade contained in product has become an important internal factor that drives the evolution of the regional water cycle and affects regional water security. Traditional water cycle research, which focused on the watershed scale, is difficult to reveal the linkage, two-way feedback mechanism and co-evolution dynamic mechanism in water cycle among different regions. Starting from the phenomenon of continuous and water-intensive agricultural products export in Northwest China, this research elaborates the phenomenon, the process, the structure and their driving forces of the unitary natural water circular, nature-human society binary circular, and trading water circular within multi-regional social economic complex systems by theoretical analysis. We explicated the theoretical framework for constructing the "natural-social-trading" ternary water cycle in the inland river basin, including mode of process, driving force of water cycle, conceptual model, influencing factors and ecological environment effects. Furthermore, we discussed the frontier of water cycle research in inland river basin based on ternary water cycle model-social hydrology. We advocated that the future study on water cycle and water resources should focus more on the external forces driving the water cycle of the inland river basin and its two-way mutual feedback and co-evolution, providing theoretical references for the decision-making of water security, ecological environment security and ecological civilization construction in inland river basins.

| [1] |
[ 陆桂华, 何海. 全球水循环研究进展. 水科学进展, 2006,17(3):419-424.]
|
| [2] |
[ 王浩, 王成明, 王建华, 等. 二元年径流演化模式及其在无定河流域的应用. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2004,34(增刊):42-48.]
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
[ 程国栋. 虚拟水:中国水资源安全战略的新思路. 中国科学院院刊, 2003(4):260-265.]
|
| [5] |
[ 龙爱华. 水资源账户与社会化管理研究: 以黑河流域张掖市为例[D]. 北京: 中国科学院研究生院, 2004.]
|
| [6] |
[ 邓铭江, 石泉. 内陆干旱区水资源管理调控模式. 地球科学进展, 2014,29(9):1046-1054.]
|
| [7] |
[ 吴普特, 高学睿, 赵西宁, 等. 实体水—虚拟水“二维三元”耦合流动理论基本框架. 农业工程学报, 2016,32(12):1-10.]
|
| [8] |
[ 刘昌明. 水量转换的若干问题//刘昌明, 任鸿遵. 水量转换: 实验与计算分析. 北京: 科学出版社, 1988: 3-21.]
|
| [9] |
[ 卢德生. 四水转化关系研究. 水利学报, 1993(12):49-54.]
|
| [10] |
[ 王浩, 陈敏建, 秦大庸, 等. 西北地区水资源合理配置和承载能力研究. 郑州: 黄河水利出版社, 2003.]
|
| [11] |
[ 龙爱华. 社会水循环理论方法与应用初步研究[D]. 北京: 中国水利水电科学研究院, 2008.]
|
| [12] |
[ 王浩, 龙爱华, 于福亮, 等. 社会水循环理论基础探析I: 定义内涵与动力机制. 水利学报, 2011,42(4):379-387.]
|
| [13] |
[ 王浩, 贾仰文. 变化中的流域“自然—社会”二元水循环理论与研究方法. 水利学报, 2016,47(10):1219-1226.]
|
| [14] |
[ 刘昌明, 王中根, 杨胜天, 等. 地表物质能量交换过程中的水循环综合模拟系统(HIMS)研究进展. 地理学报, 2014,69(5):579-587.]
|
| [15] |
[ 龙爱华, 王浩, 于福亮, 等. 社会水循环理论基础探析II: 科学问题与学科前沿. 水利学报, 2011,42(5):505-513.]
|
| [16] |
[ 殷德生. 贸易与内生经济增长: 一个理论综述. 南开经济研究, 2004(6):52-58, 71.]
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
[ 朱会义, 李义. 西北干旱区耕地扩张原因的实证分析. 地理科学进展, 2011,30(5):615-620.]
|
| [19] |
[ 张翔, 张青峰, 田龙, 等. 不同粮食消费模式下西北旱区大型灌区耕地压力分析. 干旱地区农业研究, 2015,33(1):244-251.]
|
| [20] |
[ 陈敏建, 梁瑞驹, 刘玉龙. 我国二十一世纪的水和粮食问题. 水利学报, 1999(1):1-7.]
|
| [21] |
[ 张百平, 张雪芹, 郑度. 关于严格限制西北干旱区荒地开垦的若干对策与建议. 干旱区研究, 2013,30(1):1-4.]
|
| [22] |
[ 马忠, 苏守娟, 龙爱华, 等. 塔里木河流域社会经济系统水循环分析. 地球科学进展, 2018,33(8):833-841.]
|
| [23] |
[ 尉永平, 张志强, 等. 社会水文学理论、方法与应用. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017.]
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
[ 石敏俊, 张卓颖. 中国省区间投入产出模型与区际经济联系. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012.]
|
| [26] |
Water Resources in Northwest China task group of Chinese Academy of Engineering. Strategic study on allocation of water resources, conservation and upgrading of eco-environment and sustainable development in North-west China. Engineering Science, 2003,5(4):1-26.
[ 中国工程院“西北水资源” 项目组. 西北地区水资源配置生态环境建设和可持续发展战略研究. 中国工程科学, 2003,5(4):1-26.]
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
[ 韩雪, 车亮亮, 秦晓楠. 我国主要农产品虚拟水贸易风险等级评估. 经济地理, 2018,38(3):175-180.]
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
[ 李凤丽, 曲士松, 王维平, 等. 1997—2012年山东省虚拟水贸易变化及典型区生态环境响应. 灌溉排水学报, 2018,37(2):123-128.]
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
[ 邓铭江. 中国西北“水三线”空间格局与水资源配置方略. 地理学报, 2018,73(7):1189-1203.]
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |