

中国行政区划调整的尺度政治
|
王丰龙(1988-), 男, 内蒙古赤峰人, 博士, 副教授, 中国地理学会会员(S110011312M), 研究方向为政治地理学、幸福地理学和地理学思想。E-mail: flwang@iud.ecnu.edu.cn |
收稿日期: 2018-05-15
要求修回日期: 2019-07-27
网络出版日期: 2019-10-29
基金资助
国家自然科学基金项目(No.41601144)
国家自然科学基金项目(No.41271165)
国家自然科学基金项目(No.41571130)
国家社科基金重大项目(No.15ZDA032)
版权
"Politics of scale" in Chinese administrative division adjustment
Received date: 2018-05-15
Request revised date: 2019-07-27
Online published: 2019-10-29
Supported by
National Nastrual Science Foundation of China(No.41601144)
National Nastrual Science Foundation of China(No.41271165)
National Nastrual Science Foundation of China(No.41571130)
Key Program of National Social Science Foundation of China(No.15ZDA032)
Copyright
王丰龙 , 刘云刚 . 中国行政区划调整的尺度政治[J]. 地理学报, 2019 , 74(10) : 2136 -2146 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb201910013
Administrative adjustment is a hot topic in many sub-disciplines of Chinese human geography, such as administrative regional geography, historical geography and economic geography. However, with most of the research focusing on the summarization of types, processes, impacts and practices based on inductive methods and case studies, few have proposed a general theoretical framework to explain the co-evolution of administrative adjustment and power relations. This paper tries to narrow this gap by developing a heuristic theoretical model of administrative adjustment based on the perspective of "politics of scale" and proposing a typology of rescaling and the dialectics of politics of scale in administrative adjustment. Specifically, we argue that there are mainly three types of "rescaling" in administrative adjustment, i.e. the change of order in administrative hierarchy, the transformation of territorial border or size, and the emergence of new institutional arrangement based on various administrative divisions. The "politics of scale" in administrative adjustment mainly includes two supplementary processes, i.e. the political production of scale (administrative division) and the scalar fix of administrative power relations. In both processes, the strategies of up-scaling, down-scaling and rescaling are adopted by various agencies at different levels of administrative regions. We also point out that the rescaling and politics of scale in administrative adjustment are synthetical, dynamic and dialectical. First, a specific process of administrative adjustment is associated with transformations in different forms of scale. For example, establishing a municipal city usually includes both scaling-up process in terms of county becoming city and scaling-down process since the new city only incorporates part of the original region. Second, administrative division is dynamic both as the outcome of power struggling and as the foundation of future power relations. Some forms of administrative adjustment recurred in the history. Third, similar to the uncertainty principle in physics, there is a contradiction between the size of administrative region and the degree of control of that region. As a result, the political agents tend to adopt scalar strategies to run contrary to their relative position within the scalar hierarchy, i.e. the powerful agents at higher level of administration tend to adopt down-scaling strategies and the powerful agents at lower level of administration tend to adopt up-scaling strategies; however, the tendency of scalar strategies would be to the opposite for the weak agents. This paper may not only advance the research on administrative division, but also enrich the theories of "politics of scale" which are mainly proposed based on Western practices and cases.
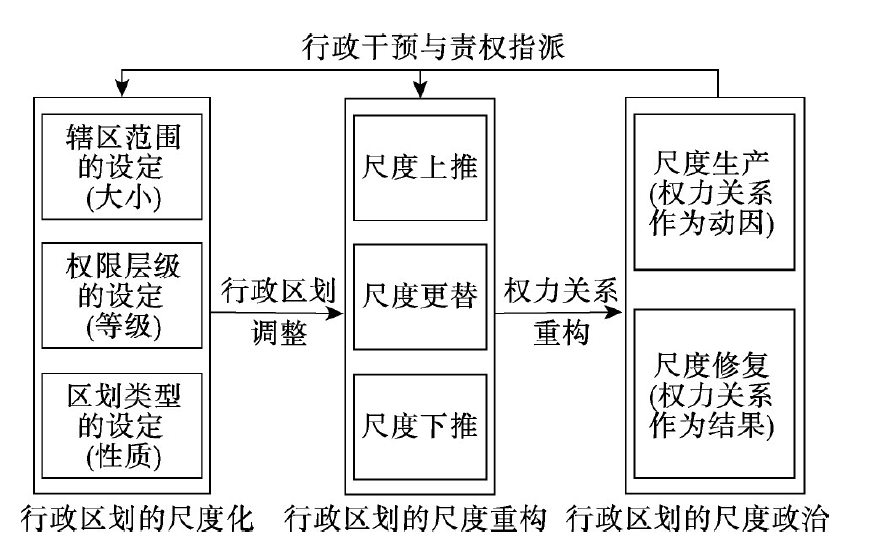
表1 基于尺度重构视角的行政区划调整类型划分Tab. 1 Typology of administrative adjustment from the perspective of rescaling |
| 管理幅员变更 | 行政等级调整 | 区划类型创设 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 尺度上推 | 城区合并; 将郊区村镇并入城区 | 县级市/县升格为地级市; 普通地级市升格为直辖市 | 设立军镇、特区或自治区; 行政公署/开发区管委会变为正式行政区 |
| 尺度下推 | 行政区拆分; 切块设市 | 撤市设区 直辖市改为省辖市 | 将行省拆分为都、布、按三司; 从省会城市变为普通城市 |
| 尺度更替 | 改朝换代后的边界重划; 从山川形便到犬牙交错 | 从市管县到省管县; 设立道、路、行省等 | 从三级制到四级制; 撤县设区、县改县级市 |
表2 行政区划调整中的尺度政治Tab. 2 Politics of scale in administrative adjustment |
| 尺度上推 | 尺度下推 | 尺度更替 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 尺度生产 | 为提升城市竞争力的城区合并; 为保持地方稳定设立羁縻府州; 迫于集团力量将监察区正式化 | “小马拉大车”导致“降级”; 为提升城市功能切块设立新城区 | 中央—地方关系与区划调整; 城市政策演变与撤县设区 |
| 尺度修复 | 设立行政特区推动领土整合; 设立封国导致“七国之乱”; 设立藩镇部分导致“安史之乱” | 通过“建分诸侯”削藩; 对少数民族“分而治之” | 撤县设区后对各自责权的争论; “省管县”的“分权悖论” |
| [1] |
[ 朱建华, 陈田, 王开泳 , 等. 改革开放以来中国行政区划格局演变与驱动力分析. 地理研究, 2015,34(2):247-258.]
|
| [2] |
[ 王开泳, 陈田 . 行政区划研究的地理学支撑与展望. 地理学报, 2018,73(4):688-700.]
|
| [3] |
[ 舒庆, 刘君德 . 一种奇异的区域经济现象: 行政区经济. 战略与管理, 1994(5):82-87.]
|
| [4] |
[ 罗震东 . 改革开放以来中国城市行政区划变更特征及趋势. 城市问题, 2008(6):77-82.]
|
| [5] |
[ 叶林, 杨宇泽 . 中国城市行政区划调整的三重逻辑: 一个研究述评. 公共行政评论, 2017,10(4):158-178.]
|
| [6] |
[ 周振鹤 . 行政区划史研究的基本概念与学术用语刍议. 复旦学报(社会科学版), 2001(3):31-36.]
|
| [7] |
[ 谢涤湘, 文吉, 魏清泉 . “撤县(市)设区”行政区划调整与城市发展. 城市规划汇刊, 2004(4):20-22.]
|
| [8] |
[ 杨沁杰, 庄汝龙 . 近二十年行政区划研究知识图谱: 基于CSSCI数据库的CiteSpaceⅢ分析. 世界地理研究, 2018,27(1):141-150.]
|
| [9] |
[ 刘君德, 靳润成, 周克瑜 . 中国政区地理. 北京: 科学出版社, 1999.]
|
| [10] |
[ 罗小龙, 殷洁, 田冬 . 不完全的再领域化与大都市区行政区划重组: 以南京市江宁撤县设区为例. 地理研究, 2010,29(10):1746-1756.]
|
| [11] |
[ 周振鹤 . 体国经野之道: 中国行政区划沿革. 上海: 上海书店出版社, 2009.]
|
| [12] |
[ 陈钊 . 地级行政区划调整对区域经济发展的影响: 以四川省为例. 经济地理, 2006,26(3):418-421.]
|
| [13] |
[ 魏衡, 魏清泉, 曹天艳 , 等. 城市化进程中行政区划调整的类型、问题与发展. 人文地理, 2009,24(6):55-58.]
|
| [14] |
[ 周伟林, 郝前进, 周吉节 . 行政区划调整的政治经济学分析: 以长江三角洲为例. 世界经济文汇, 2007(5):82-91.]
|
| [15] |
[ 范今朝, 王剑荣, 蒋瑶璐 . 试论中国当代城市化进程中的行政区划“逆向调整”现象: 以永康市芝英镇的行政区划调整过程为例. 经济地理, 2011,31(11):1798-1804.]
|
| [16] |
[ 李金龙, 邓春生 . 新中国行政区划六十年回顾与展望. 经济地理, 2009,29(12):1952-1956.]
|
| [17] |
[ 罗震东, 汪鑫, 耿磊 . 中国都市区行政区划调整: 城镇化加速期以来的阶段与特征. 城市规划, 2015,39(2):44-49.]
|
| [18] |
[ 王贤彬, 聂海峰 . 行政区划调整与经济增长. 管理世界, 2010(4):42-53.]
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
[ 左言庆, 陈秀山 . 基于尺度理论视角的中国城市行政区划调整研究. 天津行政学院学报, 2014,16(3):27-33.]
|
| [23] |
[ 王先文, 陈田 . 美国县制演化及其对中国县制改革的启示. 人文地理, 2006,21(2):109-114.]
|
| [24] |
[ 汪宇明 . 中国省直管县市与地方行政区划层级体制的改革研究. 人文地理, 2004,19(6):71-74.]
|
| [25] |
[ 范今朝 . 1979年以来浙江省行政区划调整变更的过程及作用: 兼论中国未来行政区划改革走向. 经济地理, 2004,24(4):449-453.]
|
| [26] |
[ 罗小龙, 田冬 . 行政区碎化与空间整合研究: 对江苏镇江市行政区冲突的探缘. 城市规划, 2011,35(10):18-22.]
|
| [27] |
[ 杨春 . 多中心跨境城市一区域的多层级管治: 以大珠江三角洲为例. 国际城市规划, 2008,23(1):79-84.]
|
| [28] |
[ 张践祚, 刘世定, 李贵才 . 行政区划调整中上下级间的协商博弈及策略特征: 以SS镇为例. 社会学研究, 2016, ( 3):73-99.]
|
| [29] |
[ 王丰龙, 张传勇 . 行政区划调整对大城市房价的影响研究. 地理研究, 2017,36(5):913-925.]
|
| [30] |
[ 张京祥, 陈浩, 胡嘉佩 . 中国城市空间开发中的柔性尺度调整: 南京河西新城区的实证研究. 城市规划, 2014,38(1):43-49.]
|
| [31] |
[ 刘云刚, 王丰龙 . 尺度的人文地理内涵与尺度政治: 基于1980年代以来英语圈人文地理学的尺度研究. 人文地理, 2011,26(3):1-6.]
|
| [32] |
[ 王丰龙, 刘云刚 . 尺度概念的演化与尺度的本质: 基于二次抽象的尺度认识论. 人文地理, 2015,30(1):9-15.]
|
| [33] |
[ 王丰龙, 刘云刚 . 尺度政治理论框架. 地理科学进展, 2017,36(12):1500-1509.]
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
[ 晁恒, 马学广, 李贵才 . 尺度重构视角下国家战略区域的空间生产策略: 基于国家级新区的探讨. 经济地理, 2015,35(5):1-8.]
|
| [39] |
[ 刘云刚, 王丰龙 . 三鹿奶粉事件的尺度政治分析. 地理学报, 2011,66(10):1368-1378.]
|
| [40] |
[ 陈田, 王开泳, 陈妤凡 . 行政区划调整对政区位势的影响与定量化测度: 以重庆市为例. 地理科学, 2018,38(5):654-661.]
|
| [41] |
[ 刘云刚, 王丰龙 . 中国古代政治地理思想探究. 地理科学进展, 2017,36(12):1450-1462.]
|
| [42] |
[ 许正文 . 汉州唐道的设置与分裂割据王朝的形成. 中国历史地理论丛, 2003,18(3):138-143.]
|
| [43] |
[ 刘君德, 冯春萍, 华林甫 . 中外行政区划比较研究. 上海: 华东师范大学出版社, 2002.]
|
| [44] |
[ 徐超, 孙文平 . 分权的“悖论”: “省管县”改革对居民医疗服务满意度的影响. 财经研究, 2016,42(4):38-48.]
|
| [45] |
[ 王丰龙, 曾刚 . 长江经济带研究综述与展望. 世界地理研究, 2017,26(2):62-71.]
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
[ 何苗, 丁辰 . 200个共建产业园梳理: 长三角合作共建机制现状. 2014-09-18 [2018-05-01]. .]
|
| [49] |
[ 马学广, 李鲁奇 . 尺度政治中的空间重叠及其制度形态塑造研究: 以深汕特别合作区为例. 人文地理, 2017,32(5):56-62.]
|
| [50] |
[ 刘君德, 舒庆 . 中国区域经济的新视角: 行政区经济. 改革与战略, 1996(5):1-4.]
|
| [51] |
[ 周振鹤 . 体国经野之道: 新角度下的中国行政区划沿革史. 香港: 香港中华书局, 1990.]
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |