

Drought impacts on crop yield: Progress, challenges and prospect
Received date: 2020-08-11
Request revised date: 2021-03-25
Online published: 2022-01-25
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(41801333)
National Natural Science Foundation of China(41991230)
Natural Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province(2020JQ-417)
Social Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province(2020D039)
Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities(GK201901009)
Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities(GK202003068)
Copyright
Food security, one of key components of national security, is a top priority for human survival and social development. In this study, we first sought to determine the influencing factors of crop yields and the process of drought impacts on crop yields. We then systematically reviewed the effects of droughts on major global crop yields from four aspects: field control experiments, statistical models, crop growth models, and remote sensing inversion models. Recent progress in crop yield impact assessment reveals that the current research has changed from single-hazard to multi-hazard, from single target to multiple targets, and from statistical models to a comprehensive model. A bibliometric analysis shows that the volume of research on drought impacts on crop yields has increased exponentially, and the related research theme has undergone a transformation from traditional research on crop water stress to comprehensive research on crop drought impacts and adaptation, reflecting the continuous deepening and integration of research perspectives. Agriculture, plant sciences, and environmental sciences are the three main disciplines in research on drought impacts on crop yields. We need to strengthen the application of geographical thinking, that is, systematic thinking concerning multiple factors and multiple scales to study the coupling of crop yields and water resources in the future. Finally, we suggest the following four priority areas for future research in consideration of the problems and challenges of the existing research: establishing a multi-source database of drought impact on crop yield, revealing the key process and mechanism of drought impacts on crop yields, developing a coupled macro and micro process crop growth model, and establishing a comprehensive monitoring platform system for crop yields and food security. This will help ensure sustainable agricultural development and global food security by improving monitoring, early warning, and scientific management of the impacts of droughts on crop yields.
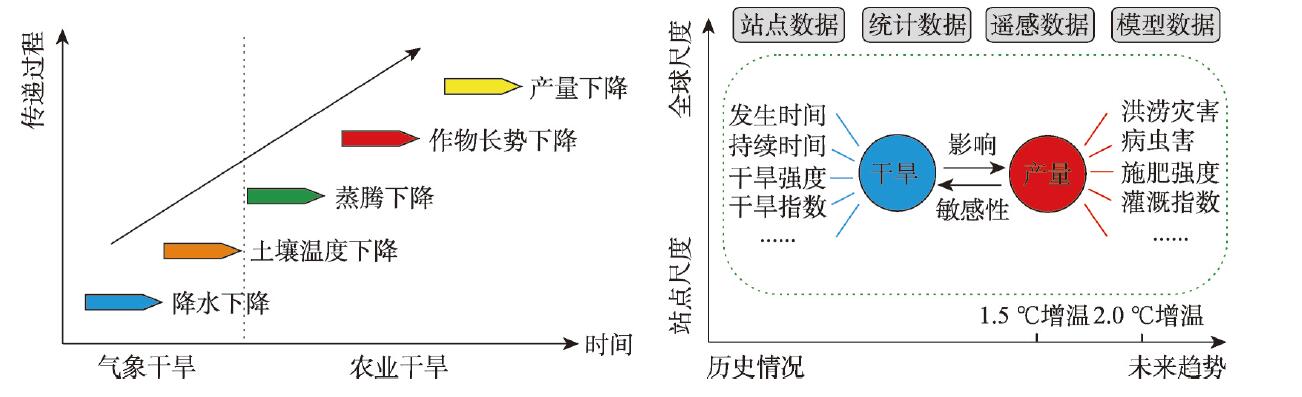
Key words: drought; crop yield; food security; research progress; research prospect
LIU Xianfeng , FU Bojie . Drought impacts on crop yield: Progress, challenges and prospect[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2021 , 76(11) : 2632 -2646 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202111003
表1 干旱对作物产量影响研究方法比较Tab. 1 Comparison of approaches on drought impact on crop yield |
| 研究手段 | 尺度 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 控制实验 | 点、样地 | ① 能够提供详细的资料 ② 实验结果精度较高 ③ 实验数据能够建模或调参 | ① 实验样地小,扩展性差 ② 试验周期长、人为影响大 ③ 实验与真实环境存在差异 |
| 统计模型 | 点、行政区 | ① 能够充分利用历史产量数据 ② 可开展不同时空尺度的研究 ③ 操作简单、重复性强 | ① 机理描述不足 ② 受统计方法影响较大 ③ 指标选取不确定性大 |
| 过程模型 | 点、空间像元 | ① 综合考虑作物生长过程 ② 能够开展定量模拟实验 ③ 能够结合气候模拟数据开展预测 | ① 内部过程简化 ② 模型参数较多 ③ 模型模拟空间分辨率较低 |
| 遥感观测 | 空间像元 | ① 能够提供空间分布信息 ② 反演结果时空分辨率高 ③ 空间范围大、重访周期短 | ① 存在长势与产量脱钩问题 ② 产量反演指标敏感性低 ③ 无法表征作物品种信息 |
感谢中国科学院空天信息创新研究院李强子研究员、西北农林科技大学何建强教授和福州大学王前锋副教授对本文成文过程中提出的宝贵建议。
| [1] |
[王浩, 杨贵羽, 杨朝晖. 水土资源约束下保障粮食安全的战略思考. 中国科学院院刊, 2013, 28(3):329-336, 321.]
|
| [2] |
[喻朝庆. 水—氮耦合机制下的中国粮食与环境安全. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2019, 49(12):2018-2036.]
|
| [3] |
[刘宪锋, 朱秀芳, 潘耀忠, 等. 农业干旱监测研究进展与展望. 地理学报, 2015, 70(11):1835-1848.]
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
[武建军, 耿广坡, 周洪奎, 等. 全球农业旱灾脆弱性及其空间分布特征. 中国科学: 地球科学, 2017, 47(6):733-744.]
|
| [6] |
[史文娇, 陶福禄, 张朝. 基于统计模型识别气候变化对农业产量贡献的研究进展. 地理学报, 2012, 67(9):1213-1222.]
|
| [7] |
[姚玉璧, 杨金虎, 肖国举, 等. 气候变暖对西北雨养农业及农业生态影响研究进展. 生态学杂志, 2018, 37(7):2170-2179.]
|
| [8] |
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. The state of food security and nutrition in the world, 2018.
|
| [9] |
[刘宪锋, 朱秀芳, 潘耀忠, 等. 近53年内蒙古寒潮时空变化特征及其影响因素. 地理学报, 2014, 69(7):1013-1024.]
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
[姚宁, 宋利兵, 刘健, 等. 不同生长阶段水分胁迫对旱区冬小麦生长发育和产量的影响. 中国农业科学, 2015, 48(12):2379-2389.]
|
| [19] |
[王书吉, 康绍忠, 李涛. 基于节水高产优质目标的冬小麦适宜水分亏缺模式. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(12):111-118.]
|
| [20] |
[宋利兵, 姚宁, 冯浩, 等. 不同生育阶段受旱对旱区夏玉米生长发育和产量的影响. 玉米科学, 2016, 24(1):63-73.]
|
| [21] |
[王密侠, 康绍忠, 蔡焕杰, 等. 调亏对玉米生态特性及产量的影响. 西北农业大学学报, 2000, 28(1):31-36.]
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
[雷廷武, 肖娟, 詹卫华, 等. 沟灌条件下不同灌溉水质对玉米产量和土壤盐分的影响. 水利学报, 2004, 35(9):118-122.]
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
[余慧倩, 张强, 孙鹏, 等. 干旱强度及发生时间对华北平原五省冬小麦产量影响. 地理学报, 2019, 74(1):87-102.]
|
| [35] |
[黄健熙, 张洁, 刘峻明, 等. 基于遥感DSI指数的干旱与冬小麦产量相关性分析. 农业机械学报, 2015, 46(3):166-173.]
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
[刘维, 李祎君, 何亮, 等. 基于SPI判定的东北春玉米生长季干旱对产量的影响. 农业工程学报, 2018, 34(22):121-127.]
|
| [38] |
[朱冉, 方一平. 柯西河流域干旱对作物产量的影响及其空间差异. 干旱区研究, 2019, 36(1):237-243.]
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
[孙扬越, 申双和. 作物生长模型的应用研究进展. 中国农业气象, 2019, 40(7):444-459.]
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
[王亚凯, 刘孟雨, 董宝娣, 等. 干旱对太行山山前平原雨养农田产量影响的模拟研究. 干旱地区农业研究, 2019, 37(2):185-194.]
|
| [57] |
[徐建文, 居辉, 梅旭荣, 等. 近30年黄淮海平原干旱对冬小麦产量的潜在影响模拟. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(6):150-158.]
|
| [58] |
[张建平, 赵艳霞, 王春乙, 等. 基于WOFOST作物生长模型的冬小麦干旱影响评估技术. 生态学报, 2013, 33(6):1762-1769.]
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
[李思佳, 孙艳楠, 李蒙, 等. 国内外农作物遥感估产的研究进展. 世界农业, 2013, 409:125-127, 131.]
|
| [62] |
[李卫国, 李花. 水稻卫星遥感估产研究现状与对策. 江苏农业科学, 2010(5):444-445.]
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
[吴炳方, 蒙继华, 李强子, 等. 全球农情遥感速报系统crop watch新进展. 地球科学进展, 2010, 25(10):1013-1022.]
|
| [67] |
[吴炳方, 张淼, 曾红伟, 等. 全球农情遥感速报系统20年. 遥感学报, 2019, 23(6):1053-1063.]
|
| [68] |
[陈仲新, 任建强, 唐华俊, 等. 农业遥感研究应用进展与展望. 遥感学报, 2016, 20(5):748-767.]
|
| [69] |
[李强子, 闫娜娜, 张飞飞, 等. 2010年春季西南地区干旱遥感监测及其影响评估. 地理学报, 2010, 65(7):771-780.]
|
| [70] |
[黄健熙, 马鸿元, 田丽燕, 等. 基于时间序列LAI和ET同化的冬小麦遥感估产方法比较. 农业工程学报, 2015, 31(4):197-203.]
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
[宋长青, 张国友, 程昌秀, 等. 论地理学的特性与基本问题. 地理科学, 2020, 40(1):6-11.]
|
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
[杨阳, 申双和, 马绎皓, 等. 干旱对作物生长的影响机制及抗旱技术的研究进展. 科技通报, 2020, 36(1):8-15.]
|
| [78] |
[易子豪, 朱德峰, 王亚梁, 等. 水稻生长对干旱的响应及其补偿效应研究进展. 中国稻米, 2020, 26(4):1-6, 9.]
|
| [79] |
[王英, 贾丽丽, 史岩. 基于IIM的干旱灾害对黑龙江省玉米供应链的级联影响研究. 灾害学, 2020, 35(3):24-28.]
|
| [80] |
[张均华, 刘建立, 张佳宝. 作物模型研究进展. 土壤, 2012, 44(1):1-9.]
|
| [81] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |