

Exploring the role of overseas industrial parks in Chinese outward foreign direct investment: A case study of Sihanoukville Special Economic Zone
Received date: 2019-10-11
Request revised date: 2020-05-18
Online published: 2020-08-25
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(41901154)
National Natural Science Foundation of China(41701138)
National Natural Science Foundation of China(41530751)
Copyright
At present, overseas industrial parks have become an important platform for economic and trade cooperation between China and other countries involved in the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), and they are playing an increasingly important role in the construction of the BRI. Most existing studies on overseas industrial parks of China focus on the economic function, while the institutional and cultural platform function need to be further explored. Based on the perspective of the institution and culture, the paper takes Sihanoukville Special Economic Zone in Cambodia as a case to analyze the operating mechanism and construction model of overseas industrial parks, and reveals the role of overseas industrial parks in promoting the outward foreign direct investment of Chinese small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). The results show that the Sihanoukville Special Economic Zone has provided a high-quality institutional environment and sufficient transnational development space for the enterprises entering the zone by constructing a multi-level coordination mechanism, creating an excellent investment environment, promoting information and resource sharing, and releasing the agglomeration economic effects. It assists enterprises in the zone to better adapt to the host country's investment, and provides more possibilities for a large number of small and medium-sized enterprises to make path breakthrough and path innovation in their overseas investments. On the basis of the case study, we believe that overseas industrial parks have played an important role in promoting Chinese small and medium-sized enterprises' overseas investment, providing buffer space and growth environment for overcoming institutional and cultural differences in Chinese enterprises' overseas investment, and played a role as an "Investor Garden".
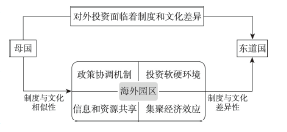
CHEN Wei , WUZHATI Yeerken , XIONG Wei , JI Qidi . Exploring the role of overseas industrial parks in Chinese outward foreign direct investment: A case study of Sihanoukville Special Economic Zone[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2020 , 75(6) : 1210 -1221 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202006009
| [1] |
[ 刘卫东, 宋周莺, 刘志高, 等. “一带一路”建设研究进展. 地理学报, 2018,74(4):620-636.]
|
| [2] |
[ 刘卫东, 田锦尘, 欧晓理, 等. “一带一路”战略研究. 北京: 商务印书馆, 2017.]
|
| [3] |
[ 刘卫东, 等. “一带一路”建设进展第三方评估报告(2013—2018年). 北京: 商务印书馆, 2019.]
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
[ 叶尔肯·吾扎提, 张薇, 刘志高. 我国在“一带一路”沿线海外园区建设模式研究. 中国科学院院刊, 2017,32(4):355-362.]
|
| [6] |
[ 赵明亮. 国际投资风险因素是否影响中国在“一带一路”国家的OFDI: 基于扩展投资引力模型的实证检验. 国际经贸探索, 2017,33(2):29-43.]
|
| [7] |
[ 李志鹏, 徐强, 闫实强. 民营企业集群式“走出去”模式与经验. 国际贸易, 2015(10):43-46.]
|
| [8] |
[ 蔡宁, 杨旭. 论企业集群和中小企业国际化发展. 中国软科学, 2002(5):54-57.]
|
| [9] |
[ 余官胜, 林俐. 企业海外集群与新晋企业对外直接投资区位选择: 基于浙江省微观企业数据. 地理研究, 2015,34(2):364-372.]
|
| [10] |
[ 李嘉楠, 龙小宁, 张相伟. 中国经贸合作新方式: 境外经贸合作区. 中国经济问题, 2016(6):64-81.]
|
| [11] |
[ 沈正平, 简晓彬, 赵洁. “一带一路”沿线中国境外合作产业园区建设模式研究. 国际城市规划, 2018,33(2):33-40.]
|
| [12] |
[ 王志芳, 杨莹, 林梦, 等. 中国境外经贸合作区的发展与挑战: 以赞比亚中国经济贸易合作区为例. 国际经济合作, 2018(10):83-87.]
|
| [13] |
[ 杨剑, 祁欣, 褚晓. 中国境外经贸合作区发展现状、问题与建议: 以中埃泰达苏伊士经贸合作区为例. 国际经济合作, 2019(1):118-126.]
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
[ 刘卫东. “一带一路”战略的科学内涵与科学问题. 地理科学进展, 2015,34(5):538-544.]
|
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
UNCTAD. World Investment Report 2019: Special Economic Zones. Geneva: United Nations, 2019.
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
[ 刘卫东, 等. 经济地理学思维. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013.]
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |