

The semiotic mechanism of cultural landscape genes of traditional settlements
Received date: 2018-08-09
Request revised date: 2019-11-08
Online published: 2020-06-25
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(41771188)
National Natural Science Foundation of China(41771150)
Major Program of National Social Science Foundation of China(16ZDA159)
Education Bureau Research Project of Hunan Province(16A030)
Social Science Foundation of Hunan Province(17ZDB050)
Research Project of Hengyang Normal University(16D14)
Copyright
The concept of cultural landscape genes of traditional settlements (CLGTS) was proposed by Chinese scholars in 2003. Since then, CLGTS has been playing a key role in capturing the deep-level geographic features of traditional settlements. However, there is a lack of work on covering CLGTS from the perspective of semiotics. Now, people are often involved in difficulties when they are trying to explore the nature of cultural landscapes of traditional settlements through using CLGTS. Obviously, it is of great significance to explore the concepts and methods of semiotic mechanism of CLGTS under the support of semiology. To lock this issue, we outline the dialectical features of CLGTS through the following five aspects. (1) For a given traditional settlement, its whole image at the macro-scale is in accordance with its cultural landscape genes at the micro-scale. (2) For the cultural landscape gene of a given traditional settlement, its core characterizations are in accordance with its appearance features. (3) For a given traditional settlement, its self-updating mechanism at local scale is in accordance with its global characterizations. (4) CLGTS can be treated as the scientific analysis method merged with the quantitative and qualitative approaches for dissecting the cultural features of traditional settlements. (5) For a given traditional settlement, its outstanding features of cultural landscape are in accordance with its rich cultural connotation. Then, this work proves the diversity of forms and complexity of spatial structures of CLGTS through ample examples. To some extent, this reveals the nonlinearity, self-organization, as well as self-iteration features of CLGTS. Based on the above, this research presents a conceptual framework of semiotic mechanism of CLGTS. Within the framework, we further summarize the symbols' main features, classifications, and expression ways of CLGTS. Through this work, we make clear the requisite theoretical conditions of making symbols of CLGTS by employing GIS. Ultimately, based on the aforementioned conceptual framework, this paper develops a prototype program for making symbols of CLGTS. The test results of the prototype program with a case of ancient village of Hunan Province show that it can run well in serving to establish a symbol database of CLGTS for a given region. Hence, this research proves that semiotic mechanism of CLGTS will make sense of perfecting the theory of CLGTS and forwarding its digital protection.
HU Zui , DENG Yunyuan , LIU Peilin , PENG Huijun . The semiotic mechanism of cultural landscape genes of traditional settlements[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2020 , 75(4) : 789 -803 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb202004009
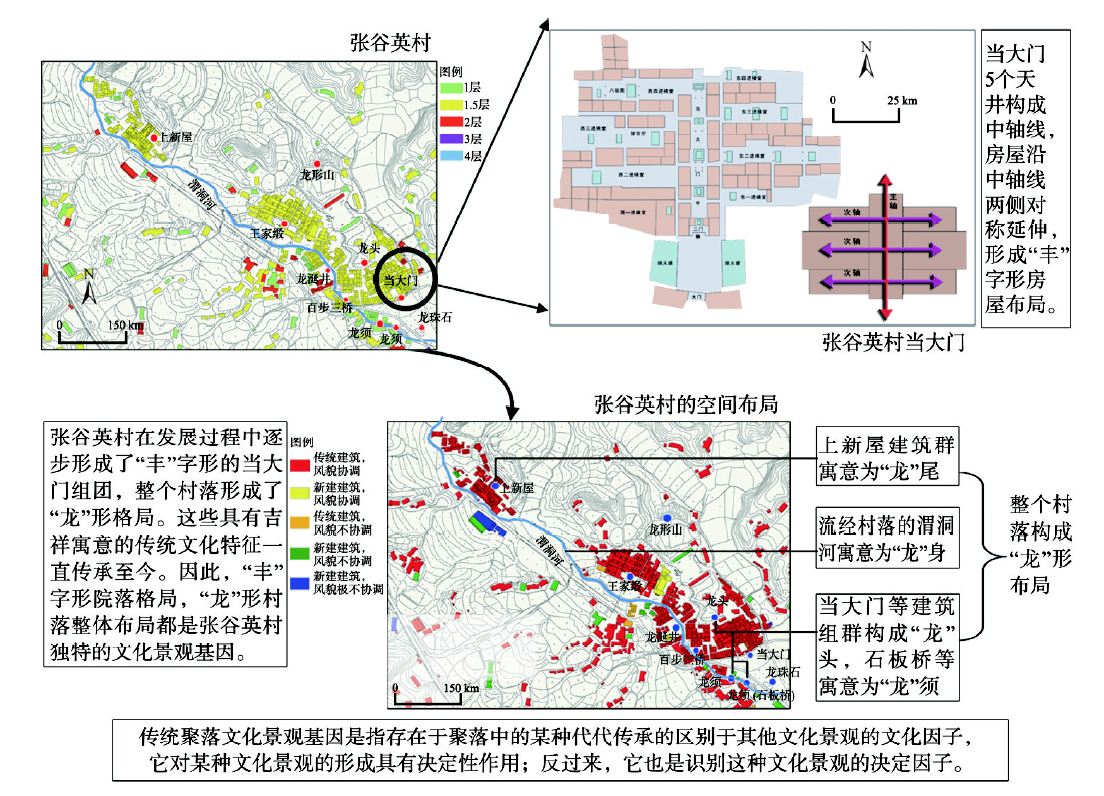
表1 文化景观基因符号的分类Tab. 1 A classification for the symbols of cultural landscape gene of traditional settlements |
| 符号类别 | 说明 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| 图形 | 通过基本图形元素的组合构成图形符号表达特定的文化景观基因的含义 | 简单符号 |
| 图片 | 直接将图片等定义为符号表达部分特殊的文化景观基因的含义 | 简单符号 |
| 文本 | 直接通过文本来描述文化景观基因的含义 | 语言符号 |
| 空间综合格局 | 结合GIS软件的地图功能来直观地表达布局类文化景观基因符号的含义 | 复合符号 |
| [1] |
[ 陶伟, 程明洋, 符文颖 . 城市化进程中广州城中村传统宗族文化的重构. 地理学报, 2015,70(12):1987-2000.]
|
| [2] |
[ 严钧, 黄颖哲, 任晓婷 . 传统聚落人居环境保护对策研究. 四川建筑科学研究, 2009,35(5):223-227.]
|
| [3] |
Central Government of China. Pact of historic and cultural cities, towns and villages. China Place Name, 2008(5):54-57.
[中华人民共和国国务院. 历史文化名城名镇名村保护条例. 中国地名, 2008(5):54-57.]
|
| [4] |
[ 赵勇, 唐渭荣, 龙丽民 , 等. 我国历史文化名镇名村保护的回顾和展望. 建筑学报, 2012(6):12-17.]
|
| [5] |
[ 胡明星, 董卫 . 基于GIS的古村落保护管理信息系统. 武汉大学学报(工学版), 2003,36(3):53-56.
|
| [6] |
[ 何川 . 湘南传统聚落生态单元的构建经验探索. 建筑科学, 2008,24(2):12-16, 35.]
|
| [7] |
[ 刘沛林 . “景观信息链”理论及其在文化旅游地规划中的运用. 经济地理, 2008,28(6):1035-1039.]
|
| [8] |
[ 张剑 . 从东楮岛村看传统聚落建筑本土化设计的低碳思维. 装饰, 2015(3):132-133.]
|
| [9] |
[ 郭武, 关菁华 . 中国古建筑的L系统建模新方法. 计算机应用研究, 2012,29(2):789-792.]
|
| [10] |
[ 赵毅衡 . 符号学与文化意义阐释. 中国人民大学学报, 2015(1):1.]
|
| [11] |
[ 姚锡凡, 李彬, 董晓倩 , 等. 符号学视角下的智慧制造系统集成框架. 计算机集成制造系统, 2014,20(11):2734-2742.]
|
| [12] |
[ 单筱秋 . 浅议图形符号在人机交互界面中的应用. 南京艺术学院学报(美术与设计), 2017(6):185-187.]
|
| [13] |
[ 周煜啸, 罗仕鉴, 陈根才 . 基于设计符号学的图标设计. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2012,24(10):1319-1328.]
|
| [14] |
[ 王旳 . 传统聚落结构中的空间概念. 2版. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2016.]
|
| [15] |
[ 曾莉, 唐雪琼 . 近年来我国村落文化景观研究进展与展望. 南京艺术学院学报(美术与设计), 2017(3):187-191.]
|
| [16] |
[ 章欣欣, 何原荣 . 采用Oracle的Google地图兴趣点抓取和发布的WebGIS系统. 华侨大学学报(自然科学版), 2015,36(6):659-662.]
|
| [17] |
[ 王君怡, 林岚, 高华 , 等. 大学生旅游地图空间符号认知的群体差异研究: 基于眼动实验数据分析. 旅游学刊, 2016,31(3):97-105.]
|
| [18] |
[ 沈雪燕, 黄中和, 何宗宜 . 地铁导向图的兴趣点选取及符号设计. 测绘通报, 2016(10):93-96.]
|
| [19] |
[ 田江鹏, 游雄, 贾奋励 , 等. 地图符号的认知语义分析与动态生成. 测绘学报, 2017,46(7):928-938.]
|
| [20] |
[ 焦东来, 张海涛, 闾国年 , 等. 地图符号服务与地图服务的耦合. 中国图象图形学报, 2013,18(9):1190-1196.]
|
| [21] |
[ 郑束蕾, 陈毓芬, 杨春雷 , 等. 地图个性化认知适合度的眼动试验评估. 测绘学报, 2015,44(S0):27-35.]
|
| [22] |
[ 何晶, 张红, 曹炜威 , 等. 地图符号拓扑紧凑性和异质性信息测度. 测绘科学, 2017,42(1):131-135.]
|
| [23] |
[ 郭星辰, 佘江峰 . 多细节层次的三维植被符号设计. 测绘科学, 2016,41(6):48-52.]
|
| [24] |
[ 何海威, 钱海忠, 李永胜 , 等. 二维码在纸质旅游地图符号设计中的应用. 辽宁工程技术大学学报(自然科学版), 2014,33(10):1392-1396.]
|
| [25] |
[ 王玉晶, 江南, 张亚军 , 等. 基于图例元的统计专题地图图例符号自动生成模型的研究. 测绘科学技术学报, 2015,32(6):635-639.]
|
| [26] |
[ 焦东来, 苗立志, 朱彩英 . 基于映射方法的动态地图符号设计与实现. 南京邮电大学学报(自然科学版), 2012,32(6):27-30.]
|
| [27] |
[ 胡最, 汤国安, 闾国年 . GIS作为新一代地理学语言的特征. 地理学报, 2012,67(7):867-877.]
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
[ 胡最, 刘沛林 . 中国传统聚落景观基因组图谱特征. 地理学报, 2015,70(10):1592-1605.]
|
| [30] |
[ 胡最, 刘沛林, 曹帅强 . 湖南省传统聚落景观基因的空间特征. 地理学报, 2013,68(2):219-231.]
|
| [31] |
[ 刘沛林, 刘春腊, 邓运员 , 等. 中国少数民族传统聚落景观特征及其基因分析. 地理科学, 2010,30(6):810-817.]
|
| [32] |
[ 张鸽娟, 徐娅, 韩怡 . 过渡性地理环境下的陕南古镇景观基因分析与表达研究. 西北大学学报(自然科学版), 2014,44(4):661-665.]
|
| [33] |
[ 王兴中, 李胜超, 李亮 , 等. 地域文化基因再现及人本观转基因空间控制理念. 人文地理, 2014,29(6):1-9.]
|
| [34] |
[ 胡最, 闵庆文, 刘沛林 . 农业文化遗产的文化景观特征识别探索: 以紫鹊界、上堡和联合梯田系统为例. 经济地理, 2018,38(2):80-87.]
|
| [35] |
[ 胡最, 郑文武, 刘沛林 , 等. 湖南省传统聚落景观基因组图谱的空间形态与结构特征. 地理学报, 2018,73(2):317-332.]
|
| [36] |
[ 黄琴诗, 朱喜钢, 陈楚文 . 传统聚落景观基因编码与派生模型研究: 以楠溪江风景名胜区为例. 中国园林, 2016(10):89-93.]
|
| [37] |
[ 刘沛林 . 家园的景观与基因: 传统聚落景观基因图谱的深层解读. 北京: 商务印书馆, 2014: 1-298.]
|
| [38] |
[ 史少博 . 论人类基因: 文化协同进化. 山东师范大学学报(人文社会科学版), 2009,54(5):55-58.]
|
| [39] |
[ 刘沛林 . 古村落文化景观的基因表达与景观识别. 衡阳师范学院学报(社会科学), 2003,24(4):1-8.]
|
| [40] |
[ 胡最, 刘沛林, 邓运员 , 等. 传统聚落景观基因的识别与提取方法研究. 地理科学, 2015,35(12):1518-1524.]
|
| [41] |
[ 刘沛林, 刘春腊, 邓运员 , 等. 客家传统聚落景观基因识别及其地学视角的解析. 人文地理, 2009,24(6):40-43.]
|
| [42] |
[ 刘沛林, 刘春腊, 邓运员 , 等. 我国古城镇景观基因“胞—链—形”的图示表达与区域差异研究. 人文地理, 2011,26(1):94-99.]
|
| [43] |
[ 翟文燕, 张侃侃, 常芳 . 基于地域“景观基因”理念下的古城文化空间认知结构: 以西安城市建筑风格为例. 人文地理, 2010,25(2):78-80.]
|
| [44] |
[ 胡最, 闫浩文 . 地图符号的语言学机制及其应用研究. 地理与地理信息科学, 2008,24(1):17-20.]
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |