

Evaluation on ecological effects under the sponge city construction at the Chuanzi River catchment in the Changde city, China
Received date: 2019-01-21
Request revised date: 2019-10-10
Online published: 2019-10-29
Supported by
National Natural Science Foundation of China(No.41471114)
Key Project of Hunan Provincial Social Science Achievement Review Committee(No.XSP17ZDA002)
PhD Research Startup Foundation of Hunan University of Arts and Science(No.E07017015)
Copyright
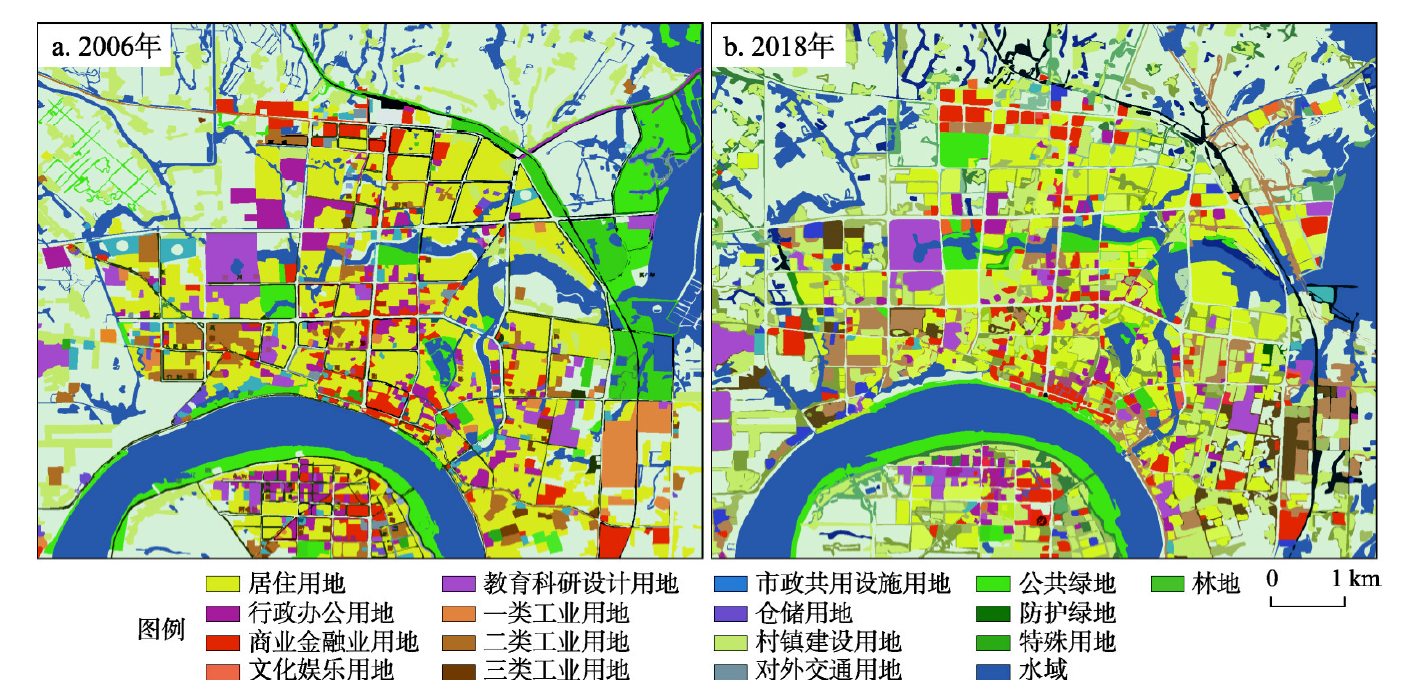
Sponge city construction (SCC) is regarded as one of the effective ways to solve the urbanization problems in China, such as waterlogging, water pollution, water shortage and heat island. Since 2015, a total of 30 pilot cities had been set up as sponge cities for providing the models of a nationwide SCC in the future. Nevertheless, the studies about the SCC mainly concentrated on its concept, planning and goal in some pilot cities, few are known about the changes of the ecological effects under the SCC. As the first city in China to accept the sponge city concept and put it into practice, the Changde city, Hunan province, with the Chuanzi River catchment as the study area, provides the ideal area to evaluate the ecological effects under the SCC in China due to a longer SCC history over the period of 2004-2019. In this study, the ecological effects under the SCC in this catchment were analyzed based on field investigation and the comparsion of the measured data of hydrology, vegetation, and temperature before and after the SCC. The results showed that the SCC effectively alleviated the waterlogging in the Changde city, but some waterlogging sites still presented at the different areas in the catchment under the rainstorm. Meanwhile, the water quality in the Chuanzi River had been generally improved from bad Ⅴ to Ⅲ grade, but there was periodically deterioration due to the pollutants enrichment in the water during the winter seasons, which were the results from both closed water system and low temperature environment. In addition, the biodiversity in the catchment had significantly increased, but it also showed some existing problems at the same time including single plant species, few plants with environmental purification functions, incomplete ecosystem and poor management. Besides, the SCC had alleviated the heat islands in summer in the Changde city to some extents. As a result, the SCC over the period of 2004-2019 in the Changde city has significantly improved the ecological effects at the Chuanzi River catchment, which provides an important ecological basis for the socio-economic development and the improvement of the living environment in this area, and provides the reference for the reasonable evaluation on the SCC effects in other pilot cities in China.
WANG Xiaqing , SUN Siyuan , YANG Ping , ZOU Xiaoyan , YI Qiaomei , PENG Baofa , XU Jianwei . Evaluation on ecological effects under the sponge city construction at the Chuanzi River catchment in the Changde city, China[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2019 , 74(10) : 2123 -2135 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb201910012
表1 2016年1月-2019年4月间穿紫河的水质类型及主要污染物Tab. 1 The water quality types and main pollutants in the Chuanzi River from January 2016 to April 2019 |
| 时间 | 水质类型 | 超标污染物 | 时间 | 水质类型 | 超标污染物 | 时间 | 水质类型 | 超标污染物 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2016.01 | Ⅴ | 总磷 | 2017.03 | Ⅱ | 无 | 2018.05 | Ⅲ | 无 |
| 2016.02 | Ⅴ | COD | 2017.04 | Ⅲ | 无 | 2018.06 | Ⅲ | 无 |
| 2016.03 | 劣Ⅴ | 氨氮 | 2017.05 | Ⅲ | 无 | 2018.07 | Ⅲ | 无 |
| 2016.04 | Ⅴ | 总磷 | 2017.06 | Ⅲ | 无 | 2018.08 | Ⅲ | 无 |
| 2016.05 | 劣Ⅴ | 总磷 | 2017.07 | Ⅲ | 无 | 2018.09 | Ⅲ | 无 |
| 2016.06 | 劣Ⅴ | 总磷 | 2017.08 | Ⅲ | 无 | 2018.10 | Ⅳ | 溶解氧 |
| 2016.07 | Ⅴ | 总磷 | 2017.09 | Ⅲ | 无 | 2018.11 | Ⅳ | 溶解氧 |
| 2016.08 | 劣Ⅴ | COD | 2017.10 | Ⅳ | 总磷 | 2018.12 | Ⅴ | 氨氮 |
| 2016.09 | Ⅳ | 无 | 2017.11 | Ⅴ | 氨氮 | 2019.01 | 劣Ⅴ | 氨氮 |
| 2016.10 | Ⅱ | 无 | 2017.12 | Ⅴ | 氨氮 | 2019.02 | Ⅲ | 无 |
| 2016.11 | Ⅲ | 无 | 2018.01 | Ⅴ | 氨氮 | 2019.03 | Ⅲ | 无 |
| 2016.12 | Ⅲ | 无 | 2018.02 | Ⅲ | 无 | 2019.04 | Ⅳ | 氨氮 |
| 2017.01 | Ⅱ | 无 | 2018.03 | Ⅳ | 氨氮 | |||
| 2017.02 | Ⅱ | 无 | 2018.04 | Ⅲ | 无 |
| [1] |
[ 俞孔坚, 李迪华, 袁弘 , 等. “海绵城市”理论与实践. 城市规划, 2015,39(6):26-36.]
|
| [2] |
[ 夏军, 张永勇, 张印 , 等. 中国海绵城市建设的水问题研究与展望. 人民长江, 2017,48(20):1-5.]
|
| [3] |
[ 仇保兴 . 海绵城市(LID)的内涵、途径与展望. 建设科技, 2015,41(3):1-7.]
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
[ 吴丹洁, 詹圣泽, 李友华 , 等. 中国特色海绵城市的新兴趋势与实践研究. 中国软科学, 2016(1):79-97.]
|
| [8] |
[ 左其亭 . 我国海绵城市建设中的水科学难题. 水资源保护, 2016,32(4):21-26.]
|
| [9] |
[ 张建云, 王银堂, 胡庆芳 . 海绵城市建设有关问题讨论. 水科学进展, 2016,27(6):793-799.]
|
| [10] |
[ 夏军, 石卫 . 变化环境下中国水安全问题研究与展望. 水利学报, 2016,47(3):292-301.]
|
| [11] |
[ 夏军, 石卫, 王强 , 等. 海绵城市建设中若干水文学问题的研讨. 水资源保护, 2017,33(1):1-8.]
|
| [12] |
[ 崔广柏, 张其成, 湛忠宇 , 等. 海绵城市建设研究进展与若干问题探讨. 水资源保护, 2016,32(2):1-4.]
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|
| [16] |
|
| [17] |
[ 张建云, 宋晓猛, 王国庆 , 等. 变化环境下城市水文学的发展与挑战: I. 城市水文效应. 水科学进展, 2014,25(4):595-601.]
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
[ 胡灿伟 . “海绵城市”重构城市水生态. 生态经济, 2015,31(7):10-13.]
|
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
|
| [22] |
|
| [23] |
[ 王新燕, 管益敏, 胡川兰 , 等. 基于"海绵城市"理念下城市水体生态化研究: 以常德市为例. 城市地理, 2016(16):110-111.]
|
| [24] |
[ 钱国辉, 苏桂明 . 雨水污水分流解决内河污染-以常德市穿紫河流域为例. 城乡建设, 2005(7):49-50.]
|
| [25] |
[ 彭赤焰, 罗帕·格罗特瓦, 郑能师 , 等. 常德市穿紫河流域生态治理实践. 景观设计学, 2017,5(1):106.]
|
| [26] |
[ 刘维斯 . 融入“海绵城市”理念的城市水系生态治理研究-以常德市穿紫河船码头为例. 中外建筑, 2017(6):136-139.]
|
| [27] |
[ 佘年, 胡坚, 王浩正 , 等. 镇江:探索智慧水务建设. 中国建设信息化, 2017(3):20-22.]
|
| [28] |
[ 熊娅, 贾立敏, 张焕祯 , 等. 温度对水解反硝化脱氮的影响. 土木建筑与环境工程, 2014,36(4):109-114.]
|
| [29] |
[ 李聪 . 西咸新区海绵城市植物选择与配置研究. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2018.]
|
| [30] |
[ 胡楠, 李雄, 戈晓宇 . 因水而变-从城市绿地系统视角谈对海绵城市体系的理性认知. 中国园林, 2015,31(6):21-25.]
|
| [31] |
[ 高菲 . 海绵城市建设: 低影响开发绿色雨水设施的植物运用. 中外建筑, 2012,28(21):45-48.]
|
| [32] |
[ 曾婷, 邓安鹏, 宋志方 . 桂林市海绵城市建设中园林植物的选择和应用. 安徽农业科学, 2018,46(8):115-117.]
|
| [33] |
[ 陈钰婷, 陈钰文, 林石狮 , 等. 广东省雨水花园适用乡土植物筛选及应用分析. 亚热带植物科学, 2017,46(3):274-280.]
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
[ 彭保发, 石忆邵, 王贺峰 , 等. 城市热岛效应的影响机理及其作用规律. 地理学报, 2013,68(11):1461-1471.]
|
| [36] |
[ 朱玲, 由阳, 程鹏飞 , 等. 海绵建设模式对城市热岛缓解效果研究. 给水排水, 2018,44(1):65-69.]
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |