

Evaluation of the GPM-based IMERG and GSMaP precipitation estimates over the Sichuan region
Received date: 2018-12-03
Request revised date: 2019-04-23
Online published: 2019-07-23
Supported by
National Key R&D Program of China(2018YFA0605402)
Copyright
The Integrated Multi-satellitE Retrievals for GPM (IMERG) and Global Satellite Mapping of Precipitation (GSMaP) are two high precisely multi-satellite precipitation estimates in the GPM era. In order to evaluate the applicability of both IMERG and GSMaP series products (IMERG_Uncal and IMERG_Cal, GSMaP_MVK and GSMaP_Gauge) over the Sichuan region in China, six statistical indices are used to systematically analyze the error characteristics of these products, benchmarked by a set of ground-based dataset from China Meterological Administration (CMA). Results show that: (1) All products show the dramatic regional difference over Sichuan at both daily and hourly scales. The GSMaP series products overestimate precipitation and the most overestimations occur over the high altitude areas located in the Western Sichuan. GSMaP_Gauge shows relatively higher correlation coefficient and lower relative bias and root mean square error due to the employment of gauge-based adjustments. On the contrary, IMERG_Uncal shows underestimation over the mountainous areas, while the relatively slight overestimation appears in the basin area with lower elevation at both daily and hourly time scales, suggesting that gauge-calibrated dataset IMERG_Cal has effectively improved the relative bias in the mountainous areas but not in the flat basin area. (2) By synthesizing the three classified statistical indices, IMERG series products exhibit better potentials in detecting precipitation events. Although GSMaP_Gauge shows a higher hit rate of precipitation, it has more false alarm ratios of precipitation. All products show better hit rate and lower false alarm rate over basin area and southern Sichuan. Furthermore, it is found that the ground-based dataset has some errors in those areas without meteorological stations, which leads to the apparent uncertainty in assessing the accuracy of satellite precipitation products over the Northwest Sichuan Plateau. (3) IMERG_Cal performs better in capturing the rainfall amounts and events compared with other products, especially for the lowest and highest rainfall intensity ranges, demonstrating its application potential for monitoring the extreme weather events. Overall, both IMERG and GSMaP estimates have relatively high uncertainties over the mountainous areas than ones over the flat basin areas. Additionally, the gauge-calibrated products obviously outperform the uncalibrated datasets. On the basis of the findings, future efforts focus on reducing and correcting the errors and biases of satellite precipitation estimates by considering both spatio-temporal characteristics and the topographical information.
Key words: IMERG; GSMaP; satellite precipitation products; Sichuan; error characteristics; terrain
ZENG Suikang , YONG Bin . Evaluation of the GPM-based IMERG and GSMaP precipitation estimates over the Sichuan region[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 2019 , 74(7) : 1305 -1318 . DOI: 10.11821/dlxb201907003
表1 卫星降水产品主要特征参数Tab. 1 Main characteristics of four satellite precipitation products |
| 降水产品 | 时空分辨率 | 覆盖范围 | 融合数据源 | 是否有站点校正 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GSMaP_MVK | 0.1º0.1º; 1 h | 准全球60ºN~60ºS | IR, PMW, DPR/GMI | 否 |
| GSMaP_Gauge | 0.1º0.1º; 1 h | 准全球60ºN~60ºS | IR, PMW, DPR/GMI | CPC站点校正 |
| IMERG_Uncal | 0.1º0.1º; 0.5 h | 全球90ºS~90ºN | IR, PMW, DPR/GMI | 否 |
| IMERG_Cal | 0.1º0.1º; 0.5 h | 全球90ºS~90ºN | IR, PMW, DPR/GMI | GPCC站点校正 |
注:① IR: Infrared Radiation data;② PMW: Passive Microwave;③ DPR/GMI: Dual-frequency Precipitation Radar/GPM Microwave Imager。 |
表2 卫星降水与地面观测降水列联表Tab. 2 Contingency table between gauge observation and satellite precipitation estimates |
| 卫星降水 | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| ≥ 阈值 | <阈值 | ||
| 地面观测 | 地面降水≥ 阈值 | H | M |
| 地面降水<阈值 | F | / | |
注:① H(Hit):降水事件被卫星正确观测到的次数;② M(Miss):卫星未观测到降水而实际发生降水的次数;③ F(False):卫星观测到降水而实际未发生降水的次数。 |
图3 GSMaP和IMERG系列产品在四川不同地形区与地面观测降水之间对比散点图Fig. 3 Scatterplots of grid-based daily precipitation between satellite products (GSMaP for top 2 rows, IMERG for bottom 2 rows) and gauge observation over different elevation areas. 1st, 2nd, and 3rd column for area I, II, and III respectively. |
图4 GSMaP和IMERG小时降水误差统计指数空间分布(a~d: CC, e~h: BIAS, i~l: RMSE)Fig. 4 Spatial distributions of statistical indices computed from GSMaP and IMERG hourly precipitation products at 0.1º×0.1º resolution over Sichuan region (a-d: CC, e-h: BIAS, i-l: RMSE) |
图5 GSMaP和IMERG降水产品的各分类统计指数空间分布(a~d: POD, e~h: FAR, i~l: CSI)Fig. 5 Spatial distributions of classified statistical indices computed from GSMaP and IMERG hourly precipitation products at 0.1º×0.1º resolution over Sichuan (a-d: POD, e-h: FAR, i-l: CSI) |
表3 卫星降水产品在不同地形区上误差评估指数统计Tab. 3 Summary of error statistical indices for satellite precipitation products in different elevation areas |
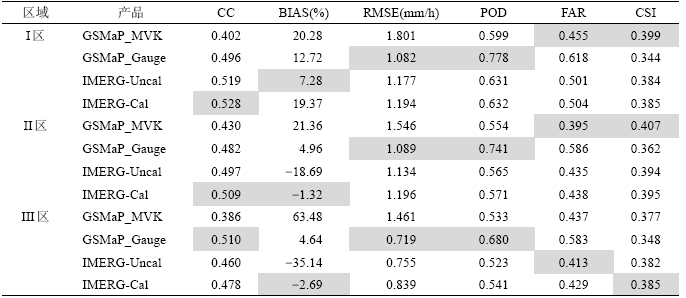 |
注:阴影部分代表各指数的最优统计值。 |
| [1] |
[ 唐国强, 龙笛, 万玮 , 等. 全球水遥感技术及其应用研究的综述与展望. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2015,45(10):1013-1023.]
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
[ 郭瑞芳, 刘元波 . 多传感器联合反演高分辨率降水方法综述. 地球科学进展, 2015,30(8):891-903.]
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
[ 江善虎, 任立良, 雍斌 , 等. TRMM卫星降水数据在洣水流域径流模拟中的应用. 水科学进展, 2014,25(5):641-649.]
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
[ 唐国强, 万玮, 曾子悦 , 等. 全球降水测量(GPM)计划及其最新进展综述. 遥感技术与应用, 2015,30(4):607-615.]
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
[ 陈晓宏, 钟睿达, 王兆礼 , 等. 新一代GPM IMERG卫星遥感降水数据在中国南方地区的精度及水文效用评估. 水利学报, 2017,48(10):1147-1156.]
|
| [16] |
[ 金晓龙, 邵华, 张弛 , 等. GPM卫星降水数据在天山山区的适用性分析. 自然资源学报, 2016,31(12):2074-2085.]
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
|
| [19] |
[ 邵远坤, 沈桐立, 游泳 , 等. 四川盆地近40年来的降水特征分析. 西南农业大学学报(自然科学版), 2005(6):749-752.]
|
| [20] |
[ 杨云川, 程根伟, 范继辉 , 等. 四川盆地及周边地区TRMM 3B42数据精度检验. 气象科学, 2013,33(5):526-535.]
|
| [21] |
[ 嵇涛, 杨华, 刘睿 , 等. TRMM卫星降水数据在川渝地区的适用性分析. 地理科学进展, 2014,33(10):1375-1386.]
|
| [22] |
[ 孙晨, 程志刚, 毛晓亮 , 等. 近44a四川地区极端气候变化趋势及特征分析. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版), 2017(1):119-126.]
|
| [23] |
[ 白莹莹, 张焱, 高阳华 , 等. 四川盆地降水变化的区域差异. 地理科学, 2011,31(4):478-484.]
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
[ 沈艳, 潘旸, 宇婧婧 , 等. 中国区域小时降水量融合产品的质量评估. 大气科学学报, 2013,36(1):37-46.]
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
[ 李麒崙, 张万昌, 易路 , 等. GPM与TRMM降水数据在中国大陆的精度评估与对比. 水科学进展, 2018,29(3):303-313.]
|
| [31] |
[ 胡庆芳, 杨大文, 王银堂 , 等. 赣江流域高分辨率卫星降水数据的精度特征与时空变化规律. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2013,56(4):447-459.]
|
| [32] |
|
| [33] |
[ 周长艳, 岑思弦, 李跃清 , 等. 四川省近50年降水的变化特征及影响. 地理学报, 2011,66(5):619-630.]
|
| [34] |
[ 刘可晶, 王文, 朱烨 , 等. 淮河流域过去60年干旱趋势特征及其与极端降水的联系. 水利学报, 2012(10):1179-1187.]
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
[ 王思梦, 王大钊, 黄昌 . GPM卫星降水数据在黑河流域的适用性评价. 自然资源学报, 2018,33(10):1847-1860.]
|
| [38] |
|
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |